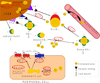
Proposed mechanism for lipoprotein remodelling in the brain
- PMID: 20470897
- PMCID: PMC3253707
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.05.001
Proposed mechanism for lipoprotein remodelling in the brain
Abstract
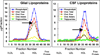
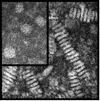
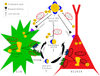
Lipoprotein remodelling in the periphery has been extensively studied. For example, the processing of nascent apoAI particles to cholesterol-loaded HDL lipoproteins during reverse cholesterol transport involves a series of enzymes, transporters in peripheral tissue, as well as other apolipoproteins and lipoproteins. These extensive modifications and interconversions are well defined. Here, we present the hypothesis that a similar process occurs within the blood brain barrier (BBB) via glia-secreted lipid-poor apoE particles undergoing remodelling to become mature central nervous system (CNS) lipoproteins. We further pose several pressing issues and future directions for the study of lipoproteins in the brain.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Formation and function of apolipoprotein E-containing lipoproteins in the nervous system.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Aug;1801(8):806-18. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.02.007. Epub 2010 Feb 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20170744 Review.
-
Lipid metabolism and glial lipoproteins in the central nervous system.Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(4):453-61. doi: 10.1248/bpb.34.453. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011. PMID: 21467629 Review.
-
Lipoproteins in the central nervous system.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000 Apr;903:167-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06365.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. PMID: 10818504 Review.
-
Cholesterol homeostasis in neurons and glial cells.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2005 Apr;16(2):193-212. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2005.01.005. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 15797830 Review.
-
Interactions of Lipids, Lipoproteins, and Apolipoproteins with the Blood-Brain Barrier.Pharm Res. 2021 Sep;38(9):1469-1475. doi: 10.1007/s11095-021-03098-6. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 34518942 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Subretinal drusenoid deposits in non-neovascular age-related macular degeneration: morphology, prevalence, topography, and biogenesis model.Retina. 2013 Feb;33(2):265-76. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e31827e25e0. Retina. 2013. PMID: 23266879 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Particles in Alzheimer Disease and Parkinson Disease.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2015 Jul;74(7):672-87. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0000000000000207. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26083568 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble apoE/Aβ complex: mechanism and therapeutic target for APOE4-induced AD risk.Mol Neurodegener. 2014 Jan 4;9:2. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-9-2. Mol Neurodegener. 2014. PMID: 24386905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prenatal Ethanol Exposure Up-Regulates the Cholesterol Transporters ATP-Binding Cassette A1 and G1 and Reduces Cholesterol Levels in the Developing Rat Brain.Alcohol Alcohol. 2014 Nov;49(6):626-34. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agu049. Epub 2014 Jul 31. Alcohol Alcohol. 2014. PMID: 25081040 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid-β pathology and APOE genotype modulate retinoid X receptor agonist activity in vivo.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 31;289(44):30538-30555. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.600833. Epub 2014 Sep 12. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25217640 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duffy D, Rader DJ. Emerging therapies targeting high-density lipoprotein metabolism and reverse cholesterol transport. Circulation. 2006;113:1140–1150. - PubMed
-
- Chang TY, Chang CC, Ohgami N, Yamauchi Y. Cholesterol sensing, trafficking, and esterification. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:129–157. - PubMed
-
- Brewer HB, Jr, Santamarina-Fojo S. New insights into the role of the adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporters in high-density lipoprotein metabolism and reverse cholesterol transport. Am J Cardiol. 2003;91:3E–11E. - PubMed
-
- Li WH, Tanimura M, Luo CC, Datta S, Chan L. The apolipoprotein multigene family: biosynthesis, structure, structure-function relationships, and evolution. J. Lipid Res. 1998;29:245–571. - PubMed
-
- Herz J, Willnow TE. Functions of the LDL receptor gene family. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994;737:14–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

