Characterization of the recalcitrant CYP1 phenotype found in Atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) inhabiting a Superfund site on the Elizabeth River, VA
- PMID: 20471113
- PMCID: PMC2883677
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.03.015
Characterization of the recalcitrant CYP1 phenotype found in Atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) inhabiting a Superfund site on the Elizabeth River, VA
Abstract
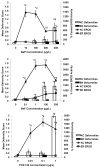
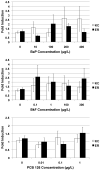
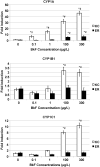
Fundulus heteroclitus (Atlantic killifish) found at the Atlantic Wood Industries Superfund site on the Elizabeth River (ER) in Portsmouth, VA (USA), have been shown to be resistant to the teratogenic effects of creosote-contaminated sediments found at this highly contaminated site. Many of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) found at the ER are known to activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR), and are thought to mediate their toxic effects through this pathway. Activation of the AHR results in the induction of several Phase I and II metabolic enzymes. It has been previously shown that the AHR of killifish from the ER are refractory to induction by AHR agonists. To more fully characterize this altered AHR response, we exposed embryos from the ER and from a reference site on King's Creek, VA (KC) to two PAHs, benzo[alpha]pyrene (BaP) and benzo[k]fluoranthene (BkF), and to the dioxin-like compound (DLC), 3,3',4,4',5-pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB126). We compared their developmental and molecular responses by screening the embryos for CYP1A enzyme activity, cardiac deformities, and mRNA expression of CYP1A, CYP1B1, CYP1C1, and AHR2. Basal gene expression of both CYP1A and CYP1B1 was 40% higher in the KC control embryos compared to those from the ER, while AHR2 and CYP1C1 were not significantly different between the populations. Exposure of KC embryos to BaP, BkF, and PCB126 induced CYP1A activity and cardiac deformities. In contrast, CYP1A activity was induced in ER embryos only in response to BkF exposure, although this induction in ER embryos was significantly lower than that observed in KC fish at comparable concentrations. ER embryos did not develop cardiac deformities in response to any of the chemicals tested. CYP1A, CYP1B1 and CYP1C1 mRNA were all significantly induced in the KC embryos after exposure to BaP, BkF and PCB126. Exposure to BaP and BkF in ER embryos resulted in a significant induction of CYP1A mRNA, albeit significantly lower than observed in KC fish. Interestingly, BaP exposure resulted in induction of CYP1B1 at comparable levels in embryos from both populations. CYP1s were not induced in ER embryos in response to PCB126, nor was CYP1C1 for any treatment examined. Additionally, AHR2 was not significantly induced for any of the treatment groups. This study further characterizes the AHR response in killifish, and provides greater insight into the adapted ER phenotype. The ER adaptation involves the suppression of normal AHR-inducible gene expression for all three CYP1 genes, and therefore is likely an alteration in AHR signaling or control.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of CYP1A inhibition on the biotransformation of benzo[a]pyrene in two populations of Fundulus heteroclitus with different exposure histories.Aquat Toxicol. 2009 May 5;92(3):195-201. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2009.01.009. Epub 2009 Jan 31. Aquat Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19269699 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and inducibility of aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway genes in wild-caught killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) with different contaminant-exposure histories.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2003 Oct;22(10):2337-43. doi: 10.1897/02-495. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2003. PMID: 14551997
-
Compound- and mixture-specific differences in resistance to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and PCB-126 among Fundulus heteroclitus subpopulations throughout the Elizabeth River estuary (Virginia, USA).Environ Sci Technol. 2013 Sep 17;47(18):10556-66. doi: 10.1021/es401604b. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Environ Sci Technol. 2013. PMID: 24003986 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to teratogenesis by F1 and F2 embryos of PAH-adapted Fundulus heteroclitus is strongly inherited despite reduced recalcitrance of the AHR pathway.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2014 Dec;21(24):13898-908. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-2446-7. Epub 2013 Dec 28. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24374617 Free PMC article.
-
The Elizabeth River Story: A Case Study in Evolutionary Toxicology.J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2015;18(6):259-98. doi: 10.1080/15320383.2015.1074841. Epub 2015 Oct 27. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2015. PMID: 26505693 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of the Major Vault Protein (MVP) and Cellular Vault Particles in Fish.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2017 Nov;300(11):1981-1992. doi: 10.1002/ar.23645. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2017. PMID: 28710803 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of CYP1C1 and CYP1A in Fundulus heteroclitus during PAH-induced carcinogenesis.Aquat Toxicol. 2010 Sep 15;99(4):439-47. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.06.002. Epub 2010 Jun 19. Aquat Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20621368 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary toxicology: Meta-analysis of evolutionary events in response to chemical stressors.Ecotoxicology. 2016 Dec;25(10):1858-1866. doi: 10.1007/s10646-016-1735-6. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Ecotoxicology. 2016. PMID: 27699564
-
Comparative chronic liver toxicity of benzo[a]pyrene in two populations of the atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) with different exposure histories.Environ Health Perspect. 2010 Oct;118(10):1376-81. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0901799. Epub 2010 May 25. Environ Health Perspect. 2010. PMID: 20501349 Free PMC article.
-
An epigenetic memory at the CYP1A gene in cancer-resistant, pollution-adapted killifish.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 24;15(1):3033. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82740-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39856074 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdulla D, Renton KW. [beta]-Adrenergic receptor modulation of the LPS-mediated depression in CYP1A activity in astrocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005;69:741–750. - PubMed
-
- Andreasen EA, Spitsbergen JM, Tanguay RL, Stegeman JJ, Heideman W, Peterson RE. Tissue-specific expression of AHR2, ARNT2, and CYP1A in zebrafish embryos and larvae: Effects of developmental stage and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin exposure. Toxicol. Sci. 2002;68:403–419. - PubMed
-
- Armknecht SL, Kaattari SL, Van Veld PA. An elevated glutathione S-transferase in crosote-resistant mummichog (Fundulus heteroclitus) Aquat. Toxicol. 1998;41:1–16.
-
- Arzuaga X, Elskus A. Evidence for resistance to benzo[a]pyrene and 3,4,3′4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl in a chronically polluted Fundulus heteroclitus population. Mar. Environ. Res. 2002;54:247–51. - PubMed
-
- Atz JW. Fundulus heteroclitus in the laboratory: A history. Am. Zoologist. 1986;26:111–120.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

