HIV-1 Tat and host AFF4 recruit two transcription elongation factors into a bifunctional complex for coordinated activation of HIV-1 transcription
- PMID: 20471948
- PMCID: PMC3085314
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.04.013
HIV-1 Tat and host AFF4 recruit two transcription elongation factors into a bifunctional complex for coordinated activation of HIV-1 transcription
Abstract
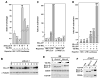
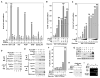
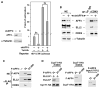
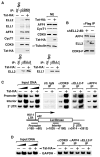
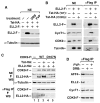
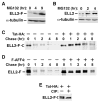
Recruitment of the P-TEFb kinase by HIV-1 Tat to the viral promoter triggers the phosphorylation and escape of RNA polymerase II from promoter-proximal pausing. It is unclear, however, if Tat recruits additional host factors that further stimulate HIV-1 transcription. Using a sequential affinity-purification scheme, we have identified human transcription factors/coactivators AFF4, ENL, AF9, and elongation factor ELL2 as components of the Tat-P-TEFb complex. Through the bridging functions of Tat and AFF4, P-TEFb and ELL2 combine to form a bifunctional elongation complex that greatly activates HIV-1 transcription. Without Tat, AFF4 can mediate the ELL2-P-TEFb interaction, albeit inefficiently. Tat overcomes this limitation by bringing more ELL2 to P-TEFb and stabilizing ELL2 in a process that requires active P-TEFb. The ability of Tat to enable two different classes of elongation factors to cooperate and coordinate their actions on the same polymerase enzyme explains why Tat is such a powerful activator of HIV-1 transcription.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bitoun E, Oliver PL, Davies KE. The mixed-lineage leukemia fusion partner AF4 stimulates RNA polymerase II transcriptional elongation and mediates coordinated chromatin remodeling. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:92–106. - PubMed
-
- Chao S-H, Price DH. Flavopiridol inactivates P-TEFb and blocks most RNA polymerase II transcription in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:31793–31799. - PubMed
-
- De Falco G, Bagella L, Claudio PP, De Luca A, Fu Y, Calabretta B, Sala A, Giordano A. Physical interaction between CDK9 and B-Myb results in suppression of B-Myb gene autoregulation. Oncogene. 2000;19:373–379. - PubMed
-
- Eissenberg JC, Shilatifard A, Dorokhov N, Michener DE. Cdk9 is an essential kinase in Drosophila that is required for heat shock gene expression, histone methylation and elongation factor recruitment. Mol Genet Genomics. 2007;277:101–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

