Targeting the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway: physiological feedback and drug response
- PMID: 20472680
- PMCID: PMC2912210
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-3064
Targeting the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway: physiological feedback and drug response
Abstract
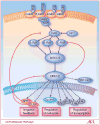
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway activation is a frequent event in human cancer and is often the result of activating mutations in the BRAF and RAS oncogenes. Targeted inhibitors of BRAF and its downstream effectors are in various stages of preclinical and clinical development. These agents offer the possibility of greater efficacy and less toxicity than current therapies for tumors driven by oncogenic mutations in the MAPK pathway. Early clinical results with the BRAF-selective inhibitor PLX4032 suggest that this strategy will prove successful in a select group of patients whose tumors are driven by V600E BRAF. Relief of physiologic feedback upon pathway inhibition may, however, attenuate drug response and contribute to the development of acquired resistance. An improved understanding of the adaptive response of cancer cells to MAPK pathway inhibition may thus aid in the identification of those patients most likely to respond to targeted pathway inhibitors and provide a rational basis for tailored combination strategies.
Figures
References
-
- McCormick F. Signal transduction. How receptors turn Ras on. Nature. 1993;363:15–6. - PubMed
-
- Morrison DK, Cutler RE. The complexity of Raf-1 regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997;9:174–9. - PubMed
-
- Chong H, Vikis HG, Guan KL. Mechanisms of regulating the Raf kinase family. Cell Signal. 2003;15:463–9. - PubMed
-
- Moodie SA, Willumsen BM, Weber MJ, Wolfman A. Complexes of Ras. GTP with Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Science. 1993;260:1658–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

