Microtubule-dependent mRNA transport in fungi
- PMID: 20472693
- PMCID: PMC2901667
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00030-10
Microtubule-dependent mRNA transport in fungi
Abstract
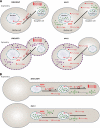
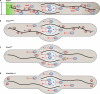
The localization and local translation of mRNAs constitute an important mechanism to promote the correct subcellular targeting of proteins. mRNA localization is mediated by the active transport of mRNPs, large assemblies consisting of mRNAs and associated factors such as RNA-binding proteins. Molecular motors move mRNPs along the actin or microtubule cytoskeleton for short-distance or long-distance trafficking, respectively. In filamentous fungi, microtubule-based long-distance transport of vesicles, which are involved in membrane and cell wall expansion, supports efficient hyphal growth. Recently, we discovered that the microtubule-mediated transport of mRNAs is essential for the fast polar growth of infectious filaments in the corn pathogen Ustilago maydis. Combining in vivo UV cross-linking and RNA live imaging revealed that the RNA-binding protein Rrm4, which constitutes an integral part of the mRNP transport machinery, mediates the transport of distinct mRNAs encoding polarity factors, protein synthesis factors, and mitochondrial proteins. Moreover, our results indicate that microtubule-dependent mRNA transport is evolutionarily conserved from fungi to higher eukaryotes. This raises the exciting possibility of U. maydis as a model system to uncover basic concepts of long-distance mRNA transport.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

