Glutaredoxin 1 regulates cigarette smoke-mediated lung inflammation through differential modulation of I{kappa}B kinases in mice: impact on histone acetylation
- PMID: 20472709
- PMCID: PMC2928604
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00426.2009
Glutaredoxin 1 regulates cigarette smoke-mediated lung inflammation through differential modulation of I{kappa}B kinases in mice: impact on histone acetylation
Abstract
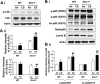
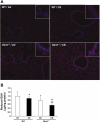
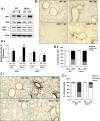
Glutaredoxin 1 (Glrx1) is a small dithiol protein that regulates the cellular redox state and redox-dependent signaling pathways via modulation of protein glutathionylation. IkappaB kinase (IKK), an essential enzyme for NF-kappaB activation, can be subjected to S-glutathionylation leading to alteration of its activity. However, the role of Glrx1 in cigarette smoke (CS)-induced lung inflammation and chromatin modifications are not known. We hypothesized that Glrx1 regulates the CS-induced lung inflammation and chromatin modifications via differential regulation of IKKs by S-glutathionylation in mouse lung. Glrx1 knockout (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice were exposed to CS for 3 days and determined the role of Glrx1 in regulation of proinflammatory response in the lung. Neutrophil influx in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and proinflammatory cytokine release in lung were increased in Glrx1 KO mice compared with WT mice exposed to CS, which was associated with augmented nuclear translocation of RelA/p65 and its phospho-acetylation. Interestingly, phosphorylated and total levels of IKKalpha, but not total and phosphorylated IKKbeta levels, were increased in lungs of Glrx1 KO mice compared with WT mice exposed to CS. Ablation of Glrx1 leads to increased CS-induced IKKbeta glutathionylation rendering it inactive, whereas IKKalpha was activated resulting in increased phospho-acetylation of histone H3 in mouse lung. Thus, targeted disruption of Glrx1 regulates the lung proinflammatory response via histone acetylation specifically by activation of IKKalpha in response to CS exposure. Overall, our study suggests that S-glutathionylation and phosphorylation of IKKalpha plays an important role in histone acetylation on proinflammatory gene promoters and NF-kappaB-mediated abnormal and sustained lung inflammation in pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory lung diseases.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

