mTOR signaling in glioblastoma: lessons learned from bench to bedside
- PMID: 20472883
- PMCID: PMC2940679
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/noq052
mTOR signaling in glioblastoma: lessons learned from bench to bedside
Abstract
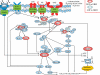
Phosphatidyl-inositol-3 kinases (PI3Ks) constitute a family of intracellular lipid kinases that are frequently hyperactivated in glioblastoma. The PI3K complex links growth factor signaling with cellular proliferation, differentiation, metabolism, and survival. Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) acts both as a downstream effector and upstream regulator of PI3K, thus highlighting its importance in glioblastoma. This review highlights laboratory and clinical evidence of mTOR's role in glioblastoma. Mechanisms of escape from mTOR inhibition are also discussed, as well as future clinical strategies of mTOR inhibition.
Figures
References
-
- Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, et al. Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev. 2007;21:2683–2710. doi:10.1101/gad.1596707. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–996. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa043330. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:606–619. doi:10.1038/nrg1879. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chalhoub N, Zhu G, Zhu X, Baker SJ. Cell type specificity of PI3K signaling in Pdk1- and Pten-deficient brains. Genes Dev. 2009;23:1619–1624. doi:10.1101/gad.1799609. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vivanco I, Sawyers CL. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:489–501. doi:10.1038/nrc839. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous