ABCA1 promotes the efflux of bacterial LPS from macrophages and accelerates recovery from LPS-induced tolerance
- PMID: 20472936
- PMCID: PMC2918449
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M007435
ABCA1 promotes the efflux of bacterial LPS from macrophages and accelerates recovery from LPS-induced tolerance
Abstract
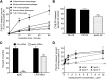
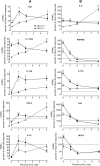
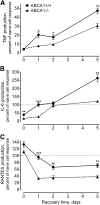
Macrophages play important roles in both lipid metabolism and innate immunity. We show here that macrophage ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1), a transporter known for its ability to promote apolipoprotein-dependent cholesterol efflux, also participates in the removal of an immunostimulatory bacterial lipid, lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Whereas monocytes require an exogenous lipoprotein acceptor to remove cell-associated LPS, macrophages released LPS in the absence of an exogenous acceptor by a mechanism that was driven, in part, by endogenous apolipoprotein E (apoE). Agents that increased ABCA1 expression increased LPS efflux from wild-type but not ABCA1-deficient macrophages. Preexposure of peritoneal macrophages to LPS for 24 h increased the expression of ABCA1 and increased LPS efflux with a requirement for exogenous apolipoproteins due to suppression of endogenous apoE production. In contrast, LPS preconditioning of ABCA1-deficient macrophages significantly decreased LPS efflux and led to prolonged retention of cell-surface LPS. Although the initial response to LPS was similar in wild-type and ABCA1-deficient macrophages, LPS-induced tolerance was greater and more prolonged in macrophages that lacked ABCA1. Our results define a new role for macrophage ABCA1 in removing cell-associated LPS and restoring normal macrophage responsiveness.
Figures




References
-
- Tang C., Oram J. F. 2009. The cell cholesterol exporter ABCA1 as a protector from cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1791: 563–572. - PubMed
-
- Francone O. L., Royer L., Boucher G., Haghpassand M., Freeman A., Brees D., Aiello R. J. 2005. Increased cholesterol deposition, expression of scavenger receptors, and response to chemotactic factors in Abca1-deficient macrophages. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25: 1198–1205. - PubMed
-
- Koseki M., Hirano K. I., Masuda D., Ikegami C., Tanaka M., Ota A., Sandoval J. C., Nakagawa-Toyama Y., Sato S. B., Kobayashi T., et al. 2007. Increased lipid rafts and accelerated lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-{alpha} secretion in Abca1-deficient macrophages. J. Lipid Res. 48: 299–306. - PubMed
-
- Yvan-Charvet L., Welch C., Pagler T. A., Ranalletta M., Lamkanfi M., Han S., Ishibashi M., Li R., Wang N., Tall A. R. 2008. Increased inflammatory gene expression in ABC transporter-deficient macrophages: free cholesterol accumulation, increased signaling via toll-like receptors, and neutrophil infiltration of atherosclerotic lesions. Circulation. 118: 1837–1847. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

