A Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi plasmid induces rapid and massive apoptosis in infected macrophages
- PMID: 20473323
- PMCID: PMC4003229
- DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2010.17
A Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi plasmid induces rapid and massive apoptosis in infected macrophages
Abstract
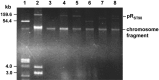
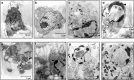
pR(ST98) is a chimeric plasmid isolated from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (S. typhi) that mediates the functions of drug resistance and virulence. Previously, we reported that Salmonella plasmid virulence (spv) genes were present in S. typhi. In our current study, we investigated whether plasmid pR(ST98) exhibits significant cytotoxicity in macrophages. pR(ST98) was transferred into the avirulent Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (S. typhimurium) strain RIA to create the transconjugant pR(ST98)/RIA. The standard S. typhimurium virulent strain SR-11, which carries a 100-kb virulence plasmid, was used as a positive control. The bacterial strains were incubated with a murine macrophage-like cell line (J774A.1) in vitro. Apoptosis of J774A.1 cells was examined by electron microscopy and flow cytometry after annexin-V/propidium iodide labeling, and the survival of Salmonella strains in J774A.1 cells was determined. Results showed that macrophages infected with strain pR(ST98)/RIA displayed greater levels of apoptosis than those infected with RIA and that pR(ST98 )may increase bacterial survival in macrophages. Further studies showed that the pR(ST98)-induced death of macrophages was associated with the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and that pR(ST98 )may activate caspase-9 and then caspase-3. The research data indicate that the virulence of bacteria that contain the pR(ST98) plasmid is enhanced; the presence of this plasmid increases the survival of the bacterial pathogen and acts through the mitochondrial pathway to mediate macrophage apoptosis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Macrophage apoptosis associated with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi plasmid.Indian J Exp Biol. 2010 Aug;48(8):773-7. Indian J Exp Biol. 2010. PMID: 21341534
-
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi plasmid pR ST98 -mediated inhibition of autophagy promotes bacterial survival in infected fibroblasts.Indian J Med Microbiol. 2012 Oct-Dec;30(4):423-30. doi: 10.4103/0255-0857.103763. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23183467
-
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi plasmid pR ST98 enhances intracellular bacterial growth and S. typhi-induced macrophage cell death by suppressing autophagy.Braz J Infect Dis. 2012 May-Jun;16(3):262-6. Braz J Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22729194
-
Evolution of the virulence plasmids of non-typhoid Salmonella and its association with antimicrobial resistance.Microbes Infect. 2006 Jun;8(7):1931-6. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2005.12.026. Epub 2006 Mar 27. Microbes Infect. 2006. PMID: 16713725 Review.
-
Effects and mechanisms of Salmonella plasmid virulence gene spv on host-regulated cell death.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Feb 2;81(3):86. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03612-0. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38305917 Review.
Cited by
-
New Insights on the Early Interaction Between Typhoid and Non-typhoid Salmonella Serovars and the Host Cells.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jul 1;12:647044. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.647044. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34276584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi plasmid impairs dendritic cell responses to infection.Curr Microbiol. 2012 Aug;65(2):133-40. doi: 10.1007/s00284-012-0136-1. Epub 2012 May 9. Curr Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22569891
-
Virulotyping of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi isolates from Pakistan: Absence of complete SPI-10 in Vi negative isolates.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 Nov 30;12(11):e0006839. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006839. eCollection 2018 Nov. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 30500817 Free PMC article.
-
Host-pathogen interaction in invasive Salmonellosis.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(10):e1002933. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002933. Epub 2012 Oct 4. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23055923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory Effects of Antimicrobial Peptide JH-3 on Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Strain CVCC541 Infection-Induced Inflammatory Cytokine Release and Apoptosis in RAW264.7 Cells.Molecules. 2019 Feb 7;24(3):596. doi: 10.3390/molecules24030596. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30736473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siddiqui FJ, Rabbani F, Hasan R, Nizami SQ, Bhutta ZA. Typhoid fever in children: some epidemiological considerations from Karachi, Pakistan. Int J Infect Dis. 2006;10:215–222. - PubMed
-
- Huang R, Mu RP. Surveillance of the antibiotic resistance and R plasmid of Salmonella typhi. Chin J Infect Dis. 1994;12:204–206.
-
- Kurita A, Gotoh H, Eguchi M, Okada N, Matsuura S, Matsui H, et al. Intracellular expression of the Salmonella plasmid virulence protein, SpvB, causes apoptotic cell death in eukaryotic cells. Microb Pathog. 2003;35:43–48. - PubMed
-
- Soto SM, Rodriguez I, Rodicio MR, Vila J, Mendoza MC. Detection of virulence determinants in clinical strains of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis and mapping on macrorestriction profiles. J Med Microbiol. 2006;55:365–373. - PubMed
-
- Huang R, Wu SY, Zhang XG, Zhang YY. Molecular analysis and identification of virulence gene on pRST98 from multi-drug resistant Salmonella typhi. Cell Mol Immunol. 2005;2:136–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

