Evolving role of MeCP2 in Rett syndrome and autism
- PMID: 20473347
- PMCID: PMC2867478
- DOI: 10.2217/epi.09.13
Evolving role of MeCP2 in Rett syndrome and autism
Abstract
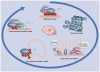
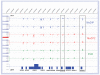
Rett syndrome is an X-linked autism-spectrum disorder caused by mutations in MECP2, encoding methyl CpG-binding protein 2. Since the discovery of MECP2 mutations as the genetic cause of Rett syndrome, the understanding of MeCP2 function has evolved. Although MeCP2 was predicted to be a global transcriptional repressor of methylated promoters, large-scale combined epigenomic approaches of MeCP2 binding, methylation and gene expression have demonstrated that MeCP2 binds preferentially to intergenic and intronic regions, and sparsely methylated promoters of active genes. This review compares the evolution of thought within two ‘classic’ epigenetic mechanisms of parental imprinting and X chromosome inactivation to that of the MeCP2 field, and considers the future relevance of integrated epigenomic databases to understanding autism and Rett syndrome.
Keywords: MeCP2; Rett syndrome; X chromosome inactivation; autism; chromatin; epigenetic; imprinting; methylation.
Figures
References
-
- Armstrong DD, Dunn K, Antalffy B. Decreased dendritic branching in frontal, motor and limbic cortex in Rett syndrome compared with trisomy 21. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1998;57(11):1013–1017. - PubMed
-
- Raymond GV, Bauman ML, Kemper TL. Hippocampus in autism: a Golgi analysis. Acta Neuropathol. 1996;91(1):117–119. - PubMed
-
- Belichenko PV, Oldfors A, Hagberg B, et al. 3-D confocal microscopy of cortical pyramidal dendrites and afferents. Neuroreport. 1994;5(12):1509–1513. - PubMed
-
- Pickett J, London E. The neuropathology of autism: a review. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2005;64(11):925–935. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong DD. Neuropathology of Rett syndrome. J. Child Neurol. 2005;20(9):747–753. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
