Tau as a biomarker of neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 20477391
- PMCID: PMC2993973
- DOI: 10.2217/17520363.2.4.363
Tau as a biomarker of neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
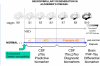
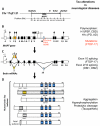
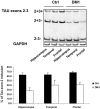
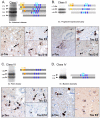
The microtubule-associated protein Tau is mainly expressed in neurons of the CNS and is crucial in axonal maintenance and axonal transport. The rationale for Tau as a biomarker of neurodegenerative diseases is that it is a major component of abnormal intraneuronal aggregates observed in numerous tauopathies, including Alzheimer's disease. The molecular diversity of Tau is very useful when analyzing it in the brain or in the peripheral fluids. Immunohistochemical and biochemical characterization of Tau aggregates in the brain allows the postmortem classification and differential diagnosis of tauopathies. As peripheral biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease in the cerebrospinal fluid, Tau proteins are now validated for diagnosis and predictive purposes. For the future, the detailed characterization of Tau in the brain and in peripheral fluids will lead to novel promising biomarkers for differential diagnosis of dementia and monitoring of therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have reported no conflict of interest. Eugeen Vanmechelen is employee from Innogenetics NV, Gent, Belgium.
Figures

References
-
- Buee L, Bussiere T, Buee-Scherrer V, Delacourte A, Hof PR. Tau protein isoforms, phosphorylation and role in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000;33(1):95–130. - PubMed
-
- Stefansson H, Helgason A, Thorleifsson G, Steinthorsdottir V, Masson G, Barnard J, Baker A, Jonasdottir A, Ingason A, Gudnadottir VG, et al. A common inversion under selection in Europeans. Nature genetics. 2005;37(2):129–137. - PubMed
-
- Schraen-Maschke S, Dhaenens CM, Delacourte A, Sablonniere B. Microtubule-associated protein tau gene: a risk factor in human neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiology of disease. 2004;15(3):449–460. - PubMed
-
- Pittman AM, Myers AJ, Duckworth J, Bryden L, Hanson M, Abou-Sleiman P, Wood NW, Hardy J, Lees A, de Silva R. The structure of the tau haplotype in controls and in progressive supranuclear palsy. Human molecular genetics. 2004;13(12):1267–1274. - PubMed
-
- Andreadis A. Tau gene alternative splicing: expression patterns, regulation and modulation of function in normal brain and neurodegenerative diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1739(2-3):91–103. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
