Viruses, microRNAs, and host interactions
- PMID: 20477536
- PMCID: PMC3621958
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.micro.112408.134243
Viruses, microRNAs, and host interactions
Abstract
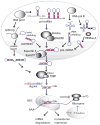
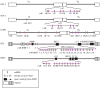
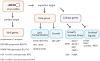
One of the most significant recent advances in biomedical research has been the discovery of the approximately 22-nt-long class of noncoding RNAs designated microRNAs (miRNAs). These regulatory RNAs provide a unique level of posttranscriptional gene regulation that modulates a range of fundamental cellular processes. Several viruses, especially herpesviruses, also encode miRNAs, and over 200 viral miRNAs have now been identified. Current evidence indicates that viruses use these miRNAs to manipulate both cellular and viral gene expression. Furthermore, viral infection can exert a profound impact on the cellular miRNA expression profile, and several RNA viruses have been reported to interact directly with cellular miRNAs and/or to use these miRNAs to augment their replication potential. Here we discuss our current knowledge of viral miRNAs and virally influenced cellular miRNAs and their relationship to viral infection.
Figures
References
-
- Anastasiadou E, Boccellato F, Vincenti S, Rosato P, Bozzoni I, et al. Epstein-Barr virus encoded LMP1 downregulates TCL1 oncogene through miR-29b. Oncogene 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

