Monocyte surface expression of Fcgamma receptor RI (CD64), a biomarker reflecting type-I interferon levels in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 20478071
- PMCID: PMC2911874
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3017
Monocyte surface expression of Fcgamma receptor RI (CD64), a biomarker reflecting type-I interferon levels in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Introduction: More than half of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients show evidence of excess type I interferon (IFN-I) production, a phenotype associated with renal disease and certain autoantibodies. However, detection of IFN-I proteins in serum is unreliable, and the measurement of interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) expression is expensive and time consuming. The aim of this study was to identify a surrogate marker for IFN-I activity in clinical samples for monitoring disease activity and response to therapy.
Methods: Monocyte surface expression of Fcgamma receptors (FcgammaRs), chemokine receptors, and activation markers were analyzed with flow cytometry in whole blood from patients with SLE and healthy controls. FcgammaR expression also was measured in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from healthy controls cultured with Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists, cytokines, or serum from SLE patients. Expression of ISGs was analyzed with real-time PCR.
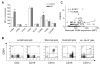
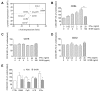
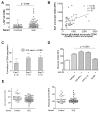
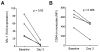
Results: Circulating CD14+ monocytes from SLE patients showed increased surface expression of FcgammaRI (CD64). The mean fluorescent intensity of CD64 staining correlated highly with the ISG expression (MX1, IFI44, and Ly6E). In vitro, IFN-I as well as TLR7 and TLR9 agonists, induced CD64 expression on monocytes from healthy controls. Exposure of monocytes from healthy controls to SLE sera also upregulated the expression of CD64 in an IFN-I-dependent manner. Decreased CD64 expression was observed concomitant with the reduction of ISG expression after high-dose corticosteroid therapy.
Conclusions: Expression of CD64 on circulating monocytes is IFN-I inducible and highly correlated with ISG expression. Flow-cytometry analysis of CD64 expression on circulating monocytes is a convenient and rapid approach for estimating IFN-I levels in SLE patients.
Figures
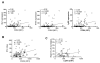
Comment in
-
A new tool for detection of type I interferon activation in systemic lupus erythematosus.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(4):138. doi: 10.1186/ar3114. Epub 2010 Aug 26. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20815919 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baechler EC, Batliwalla FM, Karypis G, Gaffney PM, Ortmann WA, Espe KJ, Shark KB, Grande WJ, Hughes KM, Kapur V, Gregersen PK, Behrens TW. Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:2610–2615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0337679100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feng X, Wu H, Grossman JM, Hanvivadhanakul P, FitzGerald JD, Park GS, Dong X, Chen W, Kim MH, Weng HH, Furst DE, Gorn A, McMahon M, Taylor M, Brahn E, Hahn BH, Tsao BP. Association of increased interferon-inducible gene expression with disease activity and lupus nephritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:2951–2962. doi: 10.1002/art.22044. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kirou KA, Lee C, George S, Louca K, Papagiannis IG, Peterson MG, Ly N, Woodward RN, Fry KE, Lau AY, Prentice JG, Wohlgemuth JG, Crow MK. Coordinate overexpression of interferon-alpha-induced genes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:3958–3967. doi: 10.1002/art.20798. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhuang H, Narain S, Sobel E, Lee PY, Nacionales DC, Kelly KM, Richards HB, Segal M, Stewart C, Satoh M, Reeves WH. Association of anti-nucleoprotein autoantibodies with upregulation of type I interferon-inducible gene transcripts and dendritic cell maturation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol. 2005;117:238–250. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2005.07.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

