Mitochondria supply membranes for autophagosome biogenesis during starvation
- PMID: 20478256
- PMCID: PMC3059894
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.04.009
Mitochondria supply membranes for autophagosome biogenesis during starvation
Abstract
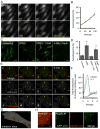
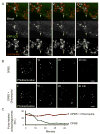
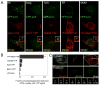
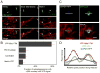
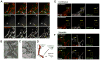
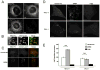
Starvation-induced autophagosomes engulf cytosol and/or organelles and deliver them to lysosomes for degradation, thereby resupplying depleted nutrients. Despite advances in understanding the molecular basis of this process, the membrane origin of autophagosomes remains unclear. Here, we demonstrate that, in starved cells, the outer membrane of mitochondria participates in autophagosome biogenesis. The early autophagosomal marker, Atg5, transiently localizes to punctae on mitochondria, followed by the late autophagosomal marker, LC3. The tail-anchor of an outer mitochondrial membrane protein also labels autophagosomes and is sufficient to deliver another outer mitochondrial membrane protein, Fis1, to autophagosomes. The fluorescent lipid NBD-PS (converted to NBD-phosphotidylethanolamine in mitochondria) transfers from mitochondria to autophagosomes. Photobleaching reveals membranes of mitochondria and autophagosomes are transiently shared. Disruption of mitochondria/ER connections by mitofusin2 depletion dramatically impairs starvation-induced autophagy. Mitochondria thus play a central role in starvation-induced autophagy, contributing membrane to autophagosomes.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Not all autophagy membranes are created equal.Cell. 2010 May 14;141(4):564-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.04.030. Cell. 2010. PMID: 20478247
-
Autophagy: From one membrane to another.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Jul;11(7):464. doi: 10.1038/nrm2920. Epub 2010 Jun 9. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20531425 No abstract available.
References
-
- Achleitner G, Gaigg B, Krasser A, Kainersdorfer E, Kohlwein SD, Perktold A, Zellnig G, Daum G. Association between the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria of yeast facilitates interorganelle transport of phospholipids through membrane contact. Eur J Biochem. 1999;264:545–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

