Re-programming of C. elegans male epidermal precursor fates by Wnt, Hox, and LIN-12/Notch activities
- PMID: 20478294
- PMCID: PMC3326348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.05.008
Re-programming of C. elegans male epidermal precursor fates by Wnt, Hox, and LIN-12/Notch activities
Abstract
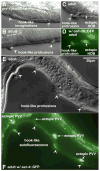
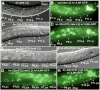
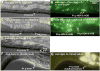
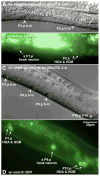
In Caenorhabditiselegans males, different subsets of ventral epidermal precursor (Pn.p) cells adopt distinct fates in a position-specific manner: three posterior cells, P(9-11).p, comprise the hook sensillum competence group (HCG) with three potential fates (1 degrees , 2 degrees , or 3 degrees ), while eight anterior cells, P(1-8).p, fuse with the hyp7 epidermal syncytium. Here we show that activation of the canonical BAR-1 beta-catenin pathway of Wnt signaling alters the competence of P(3-8).p and specifies ectopic HCG-like fates. This fate transformation requires the Hox gene mab-5. In addition, misexpression of mab-5 in P(1-8).p is sufficient to establish HCG competence among these cells, as well as to generate ectopic HCG fates in combination with LIN-12 or EGF signaling. While increased Wnt signaling induces predominantly 1 degrees HCG fates, increased LIN-12 or EGF signaling in combination with MAB-5 overexpression promotes 2 degrees HCG fates in anterior Pn.p cells, suggesting distinctive functions of Wnt, LIN-12, and EGF signaling in specification of HCG fates. Lastly, wild-type mab-5 function is necessary for normal P(9-11).p fate specification, indicating that regulation of ectopic HCG fate formation revealed in anterior Pn.p cells reflect mechanisms of pattern formation during normal hook development.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Wnt and EGF pathways act together to induce C. elegans male hook development.Dev Biol. 2009 Mar 15;327(2):419-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.12.023. Epub 2008 Dec 30. Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19154732 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of EGF and Wnt signaling during patterning of the C. elegans Bgamma/delta Equivalence Group.BMC Dev Biol. 2009 Dec 31;9:74. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-9-74. BMC Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 20042118 Free PMC article.
-
The Wnt/beta-catenin asymmetry pathway patterns the atonal ortholog lin-32 to diversify cell fate in a Caenorhabditis elegans sensory lineage.J Neurosci. 2011 Sep 14;31(37):13281-91. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6504-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21917811 Free PMC article.
-
Vulval development.WormBook. 2005 Jun 25:1-28. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.6.1. WormBook. 2005. PMID: 18050418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Variations on a theme: Hox and Wnt combinatorial regulation during animal development.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 3;2006(355):pe38. doi: 10.1126/stke.3552006pe38. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17018850 Review.
Cited by
-
Sexual Dimorphism and Sex Differences in Caenorhabditis elegans Neuronal Development and Behavior.Genetics. 2018 Mar;208(3):909-935. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300294. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29487147 Free PMC article.
-
A Cell Fate Switch in the Caenorhabditis elegans Seam Cell Lineage Occurs Through Modulation of the Wnt Asymmetry Pathway in Response to Temperature Increase.Genetics. 2020 Apr;214(4):927-939. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302896. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Genetics. 2020. PMID: 31988193 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific developmental gene expression atlas unveils dimorphic gene networks in C. elegans.Nat Commun. 2024 May 20;15(1):4273. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48369-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38769103 Free PMC article.
-
The anterior Hox gene ceh-13 and elt-1/GATA activate the posterior Hox genes nob-1 and php-3 to specify posterior lineages in the C. elegans embryo.PLoS Genet. 2022 May 2;18(5):e1010187. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010187. eCollection 2022 May. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 35500030 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical RTK-Ras-ERK signaling and related alternative pathways.WormBook. 2013 Jul 11:1-38. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.80.2. WormBook. 2013. PMID: 23908058 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chamberlin HM, Sternberg PW. The lin-3/let-23 pathway mediates inductive signalling during male spicule development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development. 1994;120:2713–2721. - PubMed
-
- Chamberlin HM, Sternberg PW. Mutations in the Caenorhabditis elegans gene vab-3 reveal distinct roles in fate specification and unequal cytokinesis in an asymmetric cell division. Dev Biol. 1995;170:679–689. - PubMed
-
- Clark SG, Chisholm AD, Horvitz HR. Control of cell fates in the central body region of C. elegans by the homeobox gene lin-39. Cell. 1993;74:43–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

