Re-programming of C. elegans male epidermal precursor fates by Wnt, Hox, and LIN-12/Notch activities
- PMID: 20478294
- PMCID: PMC3326348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.05.008
Re-programming of C. elegans male epidermal precursor fates by Wnt, Hox, and LIN-12/Notch activities
Abstract
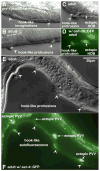
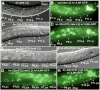
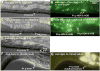
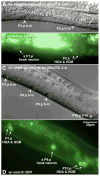
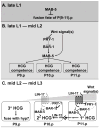
In Caenorhabditiselegans males, different subsets of ventral epidermal precursor (Pn.p) cells adopt distinct fates in a position-specific manner: three posterior cells, P(9-11).p, comprise the hook sensillum competence group (HCG) with three potential fates (1 degrees , 2 degrees , or 3 degrees ), while eight anterior cells, P(1-8).p, fuse with the hyp7 epidermal syncytium. Here we show that activation of the canonical BAR-1 beta-catenin pathway of Wnt signaling alters the competence of P(3-8).p and specifies ectopic HCG-like fates. This fate transformation requires the Hox gene mab-5. In addition, misexpression of mab-5 in P(1-8).p is sufficient to establish HCG competence among these cells, as well as to generate ectopic HCG fates in combination with LIN-12 or EGF signaling. While increased Wnt signaling induces predominantly 1 degrees HCG fates, increased LIN-12 or EGF signaling in combination with MAB-5 overexpression promotes 2 degrees HCG fates in anterior Pn.p cells, suggesting distinctive functions of Wnt, LIN-12, and EGF signaling in specification of HCG fates. Lastly, wild-type mab-5 function is necessary for normal P(9-11).p fate specification, indicating that regulation of ectopic HCG fate formation revealed in anterior Pn.p cells reflect mechanisms of pattern formation during normal hook development.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Chamberlin HM, Sternberg PW. The lin-3/let-23 pathway mediates inductive signalling during male spicule development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development. 1994;120:2713–2721. - PubMed
-
- Chamberlin HM, Sternberg PW. Mutations in the Caenorhabditis elegans gene vab-3 reveal distinct roles in fate specification and unequal cytokinesis in an asymmetric cell division. Dev Biol. 1995;170:679–689. - PubMed
-
- Clark SG, Chisholm AD, Horvitz HR. Control of cell fates in the central body region of C. elegans by the homeobox gene lin-39. Cell. 1993;74:43–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

