98% identical, 100% wrong: per cent nucleotide identity can lead plant virus epidemiology astray
- PMID: 20478884
- PMCID: PMC2880110
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2010.0056
98% identical, 100% wrong: per cent nucleotide identity can lead plant virus epidemiology astray
Abstract
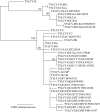
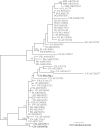
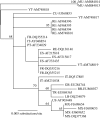
Short-form publications such as Plant Disease reports serve essential functions: the rapid dissemination of information on the geography of established plant pathogens, incidence and symptomology of pathogens in new hosts, and the discovery of novel pathogens. Many of these sentinel publications include viral sequence data, but most use that information only to confirm the virus' species. When researchers use the standard technique of per cent nucleotide identity to determine that the new sequence is closely related to another sequence, potentially erroneous conclusions can be drawn from the results. Multiple introductions of the same pathogen into a country are being ignored because researchers know fast-evolving plant viruses can accumulate substantial sequence divergence over time, even from a single introduction. An increased use of phylogenetic methods in short-form publications could speed our understanding of these cryptic second introductions and aid in control of epidemics.
Figures
References
-
- Adams M. J., Antoniw J. F., Fauquet C. M.2005Molecular criteria for genus and species discrimination within the family Potyviridae. Arch. Virol. 150, 459–479 (doi:10.1007/s00705-004-0440-6) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Akad F., Jacobi J. C., Polston J. E.2007Identification of Tomato yellow leaf curl virus and Tomato mottle virus in two counties in Alabama. Plant Dis. 91, 906 (doi:10.1094/PDIS-91-7-0906C) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Almeida R. P., Bennett G. M., Anhalt M. D., Tsai C. W., O'Grady P.2009Spread of an introduced vector-borne banana virus in Hawaii. Mol. Ecol. 18, 136–146 (doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.04009.x) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J.1990Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215, 403–410 - PubMed
-
- Amin I., Qazi J., Mansoor S., Ilyas M., Briddon R. W.2008Molecular characterizaton of Banana bunchy top virus (BBTV) from Pakistan. Virus Genes 36, 191–198 (doi:10.1007/s11262-007-0168-y) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
