Mutational fitness effects in RNA and single-stranded DNA viruses: common patterns revealed by site-directed mutagenesis studies
- PMID: 20478892
- PMCID: PMC2880115
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2010.0063
Mutational fitness effects in RNA and single-stranded DNA viruses: common patterns revealed by site-directed mutagenesis studies
Abstract
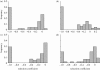
The fitness effects of mutations are central to evolution, yet have begun to be characterized in detail only recently. Site-directed mutagenesis is a powerful tool for achieving this goal, which is particularly suited for viruses because of their small genomes. Here, I discuss the evolutionary relevance of mutational fitness effects and critically review previous site-directed mutagenesis studies. The effects of single-nucleotide substitutions are standardized and compared for five RNA or single-stranded DNA viruses infecting bacteria, plants or animals. All viruses examined show very low tolerance to mutation when compared with cellular organisms. Moreover, for non-lethal mutations, the mean fitness reduction caused by single mutations is remarkably constant (0.10-0.13), whereas the fraction of lethals varies only modestly (0.20-0.41). Other summary statistics are provided. These generalizations about the distribution of mutational fitness effects can help us to better understand the evolution of RNA and single-stranded DNA viruses.
Figures
References
-
- Agudelo-Romero P., de la Iglesia F., Elena S. F.2008The pleiotropic cost of host-specialization in Tobacco etch potyvirus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 8, 806–814 (doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2008.07.010) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Azevedo R. B., Lohaus R., Srinivasan S., Dang K. K., Burch C. L.2006Sexual reproduction selects for robustness and negative epistasis in artificial gene networks. Nature 440, 87–90 (doi:10.1038/nature04488) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baba T., et al. 2006Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: the Keio collection. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2: 2006.0008 (doi:10.1038/msb4100050) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belshaw R., Gardner A., Rambaut A., Pybus O. G.2008Pacing a small cage: mutation and RNA viruses. Trends Ecol. Evol. 23, 188–193 (doi:10.1016/j.tree.2007.11.010) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bershtein S., Segal M., Bekerman R., Tokuriki N., Tawfik D. S.2006Robustness-epistasis link shapes the fitness landscape of a randomly drifting protein. Nature 444, 929–932 (doi:10.1038/nature05385) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

