Expansion of CUG RNA repeats causes stress and inhibition of translation in myotonic dystrophy 1 (DM1) cells
- PMID: 20479119
- PMCID: PMC2996918
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.09-151159
Expansion of CUG RNA repeats causes stress and inhibition of translation in myotonic dystrophy 1 (DM1) cells
Abstract
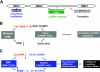
The purpose of this study was to investigate the role of the mutant CUGn RNA in the induction of stress in type 1 myotonic dystrophy (DM1) cells and in the stress-mediated inhibition of protein translation in DM1. To achieve our goals, we performed HPLC-based purification of stress granules (SGs), immunoanalysis of SGs with stress markers TIA-1, CUGBP1, and ph-eIF2, site-specific mutagenesis, and examinations of RNA-protein and protein-protein interactions in myoblasts from control and DM1 patients. The cause-and-effect relationships were addressed in stable cells expressing mutant CUG repeats. We found that the mutant CUGn RNA induces formation of SGs through the increase of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) and following inactivation of eIF2α, one of the substrates of PKR. We show that SGs trap mRNA coding for the DNA repair and remodeling factor MRG15 (MORF4L1), translation of which is regulated by CUGBP1. As the result of the trapping, the levels of MRG15 are reduced in DM1 cells and in CUG-expressing cells. These data show that CUG repeats cause stress in DM1 through the PKR-ph-eIF2α pathway inhibiting translation of certain mRNAs, such as MRG15 mRNA. The repression of protein translation by stress might contribute to the progressive muscle loss in DM1.
Figures
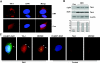
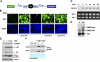

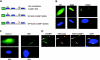


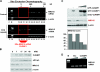
References
-
- Harper P. S. (2001) Myotonic Dystrophy, W. B. Saunders, London
-
- Aslanidis C., Jansen G., Amemiya C., Shutler G., Mahadevan M., Tsilfidis C., Clen C., Alleman J., Wormskamp N. G., Vooijs M., Buxton J., Johnson K., Sweets H. J. M., Lennon G. G., Carrano A. V. R. G., Korneluk R. G., Wieringa B., deJong P. J. (1992) Cloning of essential myotonic dystrophy region and mapping of the putative defect. Nature 355, 548–551 - PubMed
-
- Brook J. D., McCurrah M. E., Harley H. G., Buckler A. J., Church D., Aburatani H., Hunter K., Stanton V. P., Thirion J.-P., Hudson T., Sohn R., Zemelman B., Snell R. G., Rundle S. A., Crow S., Davies J., Shelbourne P., Buxton J., Jones C., Juvonen V., Johnson K., Harper P. S., Shaw D. J., Housman D. E. (1992) Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeats at the 3′ end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell 68, 799–808 - PubMed
-
- Buxton J., Shelbourne P., Davies J., Jones C., Van Tongeren T., Aslanidis C., de Jong P., Jansen G., Avret M., Riley B., Williamson R., Johnson K. (1992) Detection of an unstable fragment of DNA specific to individuals with myotonic dystrophy. Nature 355, 547–548 - PubMed
-
- Fu Y. H., Pizzuti A., Fenwick R. G., Jr., King J., Rajnarayan S., Dunne P. W., Dubel J., Nasser G. A., Ashizawa T., de Jong P., Wieringa B., Korneluk R., Perryman M. B., Epstein H. F., Caskey C. T. (1992) An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science 255, 1256–1258 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA100070/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AR044387/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025477/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG032134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AR044387-ARRA/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA100070/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AR052791/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR052791/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS063298/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- GM55188/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM055188/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AG025477/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R03 NS063298/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR044387/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

