Ric-8A and Gi alpha recruit LGN, NuMA, and dynein to the cell cortex to help orient the mitotic spindle
- PMID: 20479129
- PMCID: PMC2897540
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00394-10
Ric-8A and Gi alpha recruit LGN, NuMA, and dynein to the cell cortex to help orient the mitotic spindle
Abstract
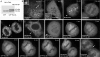
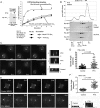
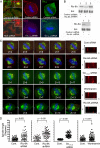
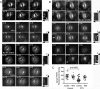
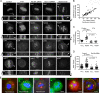
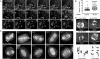
In model organisms, resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase 8 (Ric-8), a G protein alpha (G alpha) subunit guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), functions to orient mitotic spindles during asymmetric cell divisions; however, whether Ric-8A has any role in mammalian cell division is unknown. We show here that Ric-8A and G alpha(i) function to orient the metaphase mitotic spindle of mammalian adherent cells. During mitosis, Ric-8A localized at the cell cortex, spindle poles, centromeres, central spindle, and midbody. Pertussis toxin proved to be a useful tool in these studies since it blocked the binding of Ric-8A to G alpha(i), thus preventing its GEF activity for G alpha(i). Linking Ric-8A signaling to mammalian cell division, treatment of cells with pertussis toxin, reduction of Ric-8A expression, or decreased G alpha(i) expression similarly affected metaphase cells. Each treatment impaired the localization of LGN (GSPM2), NuMA (microtubule binding nuclear mitotic apparatus protein), and dynein at the metaphase cell cortex and disturbed integrin-dependent mitotic spindle orientation. Live cell imaging of HeLa cells expressing green fluorescent protein-tubulin also revealed that reduced Ric-8A expression prolonged mitosis, caused occasional mitotic arrest, and decreased mitotic spindle movements. These data indicate that Ric-8A signaling leads to assembly of a cortical signaling complex that functions to orient the mitotic spindle.
Figures
References
-
- Afshar, K., F. S. Willard, K. Colombo, C. A. Johnston, C. R. McCudden, D. P. Siderovski, and P. Gonczy. 2004. RIC-8 is required for GPR-1/2-dependent Gα function during asymmetric division of Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Cell 119:219-230. - PubMed
-
- Afshar, K., F. S. Willard, K. Colombo, D. P. Siderovski, and P. Gonczy. 2005. Cortical localization of the Gα protein GPA-16 requires RIC-8 function during Caenorhabditis elegans asymmetric cell division. Development 132:4449-4459. - PubMed
-
- Blumer, J. B., R. Kuriyama, T. W. Gettys, and S. M. Lanier. 2006. The G-protein regulatory (GPR) motif-containing Leu-Gly-Asn-enriched protein (LGN) and Giα3 influence cortical positioning of the mitotic spindle poles at metaphase in symmetrically dividing mammalian cells. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 85:1233-1240. - PubMed
-
- Busson, S., D. Dujardin, A. Moreau, J. Dompierre, and J. R. De Mey. 1998. Dynein and dynactin are localized to astral microtubules and at cortical sites in mitotic epithelial cells. Curr. Biol. 8:541-544. - PubMed
-
- Couwenbergs, C., A. C. Spilker, and M. Gotta. 2004. Control of embryonic spindle positioning and Gα activity by Caenorhabditis elegans RIC-8. Curr. Biol. 14:1871-1876. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
