Information processing at the foxa node of the sea urchin endomesoderm specification network
- PMID: 20479235
- PMCID: PMC2890477
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1004824107
Information processing at the foxa node of the sea urchin endomesoderm specification network
Abstract
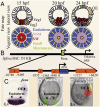
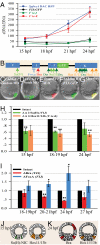
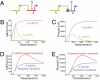
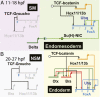
The foxa regulatory gene is of central importance for endoderm specification across Bilateria, and this gene lies at an essential node of the well-characterized sea urchin endomesoderm gene regulatory network (GRN). Here we experimentally dissect the cis-regulatory system that controls the complex pattern of foxa expression in these embryos. Four separate cis-regulatory modules (CRMs) cooperate to control foxa expression in different spatial domains of the endomesoderm, and at different times. A detailed mutational analysis revealed the inputs to each of these cis-regulatory modules. The complex and dynamic expression of foxa is regulated by a combination of repressors, a permissive switch, and multiple activators. A mathematical kinetic model was applied to study the dynamic response of foxa cis-regulatory modules to transient inputs. This study shed light on the mesoderm-endoderm fate decision and provides a functional explanation, in terms of the genomic regulatory code, for the spatial and temporal expression of a key developmental control gene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Oliveri P, Walton KD, Davidson EH, McClay DR. Repression of mesodermal fate by foxa, a key endoderm regulator of the sea urchin embryo. Development. 2006;133:4173–4181. - PubMed
-
- Boyle MJ, Seaver EC. Developmental expression of foxA and gata genes during gut formation in the polychaete annelid, Capitella sp. I. Evol Dev. 2008;10:89–105. - PubMed
-
- Hiruta J, Mazet F, Yasui K, Zhang P, Ogasawara M. Comparative expression analysis of transcription factor genes in the endostyle of invertebrate chordates. Dev Dyn. 2005;233:1031–1037. - PubMed
-
- Burtscher I, Lickert H. Foxa2 regulates polarity and epithelialization in the endoderm germ layer of the mouse embryo. Development. 2009;136:1029–1038. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

