Extracellular sulfatases support cartilage homeostasis by regulating BMP and FGF signaling pathways
- PMID: 20479257
- PMCID: PMC2890424
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0913897107
Extracellular sulfatases support cartilage homeostasis by regulating BMP and FGF signaling pathways
Abstract
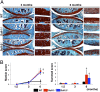
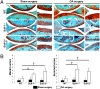
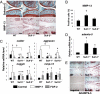
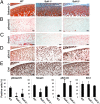
The balance between anabolic and catabolic signaling pathways is critical in maintaining cartilage homeostasis and its disturbance contributes to joint diseases such as osteoarthritis (OA). A unique mechanism that modulates the activity of cell signaling pathways is controlled by extracellular heparan endosulfatases Sulf-1 and Sulf-2 (Sulfs) that are overexpressed in OA cartilage. This study addressed the role of Sulfs in cartilage homeostasis and in regulating bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)/Smad and fibroblast growth factor (FGF)/Erk signaling in articular cartilage. Spontaneous cartilage degeneration and surgically induced OA were significantly more severe in Sulf-1(-/-) and Sulf-2(-/-) mice compared with wild-type mice. MMP-13, ADAMTS-5, and the BMP antagonist noggin were elevated whereas col2a1 and aggrecan were reduced in cartilage and chondrocytes from Sulf(-/-) mice. Articular cartilage and cultured chondrocytes from Sulf(-/-) mice showed reduced Smad1 protein expression and Smad1/5 phosphorylation, whereas Erk1/2 phosphorylation was increased. In human chondrocytes, Sulfs siRNA reduced Smad phosphorylation but enhanced FGF-2-induced Erk1/2 signaling. These findings suggest that Sulfs simultaneously enhance BMP but inhibit FGF signaling in chondrocytes and maintain cartilage homeostasis. Approaches to correct abnormal Sulf expression have the potential to protect against cartilage degradation and promote cartilage repair in OA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Goldring MB. The role of the chondrocyte in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:1916–1926. - PubMed
-
- Lyons KM, Pelton RW, Hogan BL. Patterns of expression of murine Vgr-1 and BMP-2a RNA suggest that transforming growth factor-beta-like genes coordinately regulate aspects of embryonic development. Genes Dev. 1989;3:1657–1668. - PubMed
-
- Lyons KM, Pelton RW, Hogan BL. Organogenesis and pattern formation in the mouse: RNA distribution patterns suggest a role for bone morphogenetic protein-2A (BMP-2A) Development. 1990;109:833–844. - PubMed
-
- Yi SE, Daluiski A, Pederson R, Rosen V, Lyons KM. The type I BMP receptor BMPRIB is required for chondrogenesis in the mouse limb. Development. 2000;127:621–630. - PubMed
-
- Miljkovic ND, Cooper GM, Marra KG. Chondrogenesis, bone morphogenetic protein-4 and mesenchymal stem cells. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16:1121–1130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

