Organophosphorus pesticides decrease M2 muscarinic receptor function in guinea pig airway nerves via indirect mechanisms
- PMID: 20479945
- PMCID: PMC2866713
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010562
Organophosphorus pesticides decrease M2 muscarinic receptor function in guinea pig airway nerves via indirect mechanisms
Abstract
Background: Epidemiological studies link organophosphorus pesticide (OP) exposures to asthma, and we have shown that the OPs chlorpyrifos, diazinon and parathion cause airway hyperreactivity in guinea pigs 24 hr after a single subcutaneous injection. OP-induced airway hyperreactivity involves M2 muscarinic receptor dysfunction on airway nerves independent of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition, but how OPs inhibit neuronal M2 receptors in airways is not known. In the central nervous system, OPs interact directly with neurons to alter muscarinic receptor function or expression; therefore, in this study we tested whether the OP parathion or its oxon metabolite, paraoxon, might decrease M2 receptor function on peripheral neurons via similar direct mechanisms.
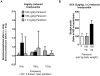
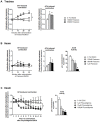
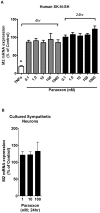
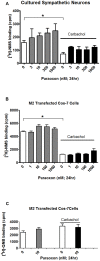
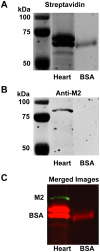
Methodology/principal findings: Intravenous administration of paraoxon, but not parathion, caused acute frequency-dependent potentiation of vagally-induced bronchoconstriction and increased electrical field stimulation (EFS)-induced contractions in isolated trachea independent of AChE inhibition. However, paraoxon had no effect on vagally-induced bradycardia in intact guinea pigs or EFS-induced contractions in isolated ileum, suggesting mechanisms other than pharmacologic antagonism of M2 receptors. Paraoxon did not alter M2 receptor expression in cultured cells at the mRNA or protein level as determined by quantitative RT-PCR and radio-ligand binding assays, respectively. Additionally, a biotin-labeled fluorophosphonate, which was used as a probe to identify molecular targets phosphorylated by OPs, did not phosphorylate proteins in guinea pig cardiac membranes that were recognized by M2 receptor antibodies.
Conclusions/significance: These data indicate that neither direct pharmacologic antagonism nor downregulated expression of M2 receptors contributes to OP inhibition of M2 function in airway nerves, adding to the growing evidence of non-cholinergic mechanisms of OP neurotoxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
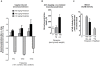
Similar articles
-
Organophosphorus insecticides induce airway hyperreactivity by decreasing neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor function independent of acetylcholinesterase inhibition.Toxicol Sci. 2005 Jan;83(1):166-76. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfi001. Epub 2004 Oct 6. Toxicol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15470232
-
The influence of sensitization on mechanisms of organophosphorus pesticide-induced airway hyperreactivity.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015 Nov;53(5):738-47. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0444OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25897622 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen sensitization influences organophosphorus pesticide-induced airway hyperreactivity.Environ Health Perspect. 2008 Mar;116(3):381-8. doi: 10.1289/ehp.10694. Environ Health Perspect. 2008. PMID: 18335107 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of organophosphorus pesticide toxicity in the context of airway hyperreactivity and asthma.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018 Oct 1;315(4):L485-L501. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00211.2018. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29952220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood cholinesterases as human biomarkers of organophosphorus pesticide exposure.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2000;163:29-111. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-6429-1_2. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2000. PMID: 10771584 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative stress resulting from exposure of a human salivary gland cells to paraoxon: an in vitro model for organophosphate oral exposure.Toxicol In Vitro. 2014 Aug;28(5):715-21. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2014.01.009. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Toxicol In Vitro. 2014. PMID: 24486155 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in neurotoxic outcomes of organophosphorus pesticides revealed via multi-dimensional screening in adult and regenerating planarians.Front Toxicol. 2022 Oct 4;4:948455. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2022.948455. eCollection 2022. Front Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36267428 Free PMC article.
-
Pioglitazone prevents obesity-related airway hyperreactivity and neuronal M2 receptor dysfunction.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2021 Jul 1;321(1):L236-L247. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00567.2020. Epub 2021 May 19. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34009030 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophil and airway nerve interactions in asthma.J Leukoc Biol. 2018 Jul;104(1):61-67. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3MR1117-426R. Epub 2018 Apr 6. J Leukoc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29633324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organophosphorus Pesticides Induce Cytokine Release from Differentiated Human THP1 Cells.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019 Nov;61(5):620-630. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0257OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30978295 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hartert TV, Peebles RS., Jr Epidemiology of asthma: the year in review. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2000;6:4–9. - PubMed
-
- Weitzman M, Gortmaker SL, Sobol AM, Perrin JM. Recent trends in the prevalence and severity of childhood asthma. Jama. 1992;268:2673–2677. - PubMed
-
- Wilhoit L, Davidson N, Supkoff D, Steggal J, Braun A, et al. Pesticide Use Analysis and Trends from 1991 to 1996. Sacramento, CA: State of California Environmental Protection Agency. PM 99-01 PM. 1999:99–01.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

