Simultaneous treatment to attain blood pressure and lipid goals and reduced CV risk burden using amlodipine/atorvastatin single-pill therapy in treated hypertensive participants in a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 20479948
- PMCID: PMC2868347
- DOI: 10.2147/vhrm.s7710
Simultaneous treatment to attain blood pressure and lipid goals and reduced CV risk burden using amlodipine/atorvastatin single-pill therapy in treated hypertensive participants in a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
TOGETHER investigated whether targeting multiple cardiovascular (CV) risk factors using single-pill amlodipine/atorvastatin (AML/ATO) and therapeutic lifestyle changes (TLC) results in greater blood pressure (BP)/lipid control and additional reduction in estimated cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk compared with blood pressure intervention only using amlodipine (AML) + TLC. TOGETHER was a 6-week, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy trial using hypertensive participants with additional CV risk factors without CVD/diabetes. Participants were randomized to either AML/ATO (5 to 10/20 mg) + TLC or AML (5 to 10 mg) + TLC. The primary end point was the difference in proportion of participants attaining both BP (<140/90 mm Hg) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) (<100 mg/dL) goals at week 6. At week 6, 67.8% of participants receiving AML/ATO + TLC attained the combined BP/LDL-C goal versus 9.6% with AML + TLC (RD [A-B]: 58.2; 95% CI [48.1 to 68.4] P < 0.001; OR: 19.0; 95% CI 9.1 to 39.6; P < 0.001). Significant reductions from baseline in LDL-C, total cholesterol and triglycerides and estimated 10-year Framingham risk were also observed. Treatment with AML/ATO was well tolerated. In conclusion, a multifactorial CV management approach is more effective in achieving combined BP/LDL-C targets as well as CV risk reduction compared with BP intervention only in this patient population.
Keywords: blood pressure; calcium channel blocker; low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; statin.
Figures

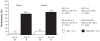


References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics 2009 Update. A Report From the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2009;119:e1–e161. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB. Fifty years of Framingham Study contributions to understanding hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2000;14:83–90. - PubMed
-
- Ansell BJ. Evidence for a combined approach to the management of hypertension and dyslipidemia. Am J Hypertens. 2005;18:1249–1257. - PubMed
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003;42:1206–1252. - PubMed
-
- NCEP ATP., III Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) JAMA. 2001;285:2486–2497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

