The outer vestibule of the Na+ channel-toxin receptor and modulator of permeation as well as gating
- PMID: 20479982
- PMCID: PMC2866490
- DOI: 10.3390/md8041373
The outer vestibule of the Na+ channel-toxin receptor and modulator of permeation as well as gating
Abstract
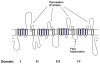
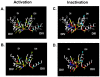
The outer vestibule of voltage-gated Na(+) channels is formed by extracellular loops connecting the S5 and S6 segments of all four domains ("P-loops"), which fold back into the membrane. Classically, this structure has been implicated in the control of ion permeation and in toxin blockage. However, conformational changes of the outer vestibule may also result in alterations in gating, as suggested by several P-loop mutations that gave rise to gating changes. Moreover, partial pore block by mutated toxins may reverse gating changes induced by mutations. Therefore, toxins that bind to the outer vestibule can be used to modulate channel gating.
Keywords: outer vestibule; rate-dependent block; saxitoxin; sodium channel; tetrodotoxin; use-dependent block.
Figures
References
-
- Sutkowski EM, Catterall WA. Beta 1 subunits of sodium channels. Studies with subunit-specific antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:12393–12399. - PubMed
-
- Isom LL, De Jongh KS, Patton DE, Reber BF, Offord J, Charbonneau H, Walsh K, Goldin AL, Catterall WA. Primary structure and functional expression of the beta 1 subunit of the rat brain sodium channel. Science. 1992;256:839–842. - PubMed
-
- Goldin AL, Snutch T, Lubbert H, Dowsett A, Marshall J, Auld V, Downey W, Fritz LC, Lester HA, Dunn R, et al. Messenger RNA coding for only the alpha subunit of the rat brain Na+ channel is sufficient for expression of functional channels in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1986;83:7503–7507. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Noda M, Shimizu S, Tanabe T, Takai T, Kayano T, Ikeda T, Takahashi H, Nakayama H, Kanaoka Y, Minamino N, et al. Primary structure of Electrophorus electricus sodium channel deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1984;312:121–127. - PubMed
-
- Bezanilla F. The voltage sensor in voltage-dependent ion channels. Physiol Rev. 2000;80:555–592. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
