β-Sitosterol: supercritical carbon dioxide extraction from sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) seeds
- PMID: 20480045
- PMCID: PMC2871141
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms11041842
β-Sitosterol: supercritical carbon dioxide extraction from sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) seeds
Abstract
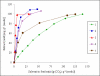
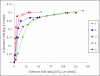
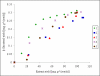
Supercritical fluid extraction represents an efficient and environmentally friendly technique for isolation of phytosterols from different plant sources. Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) seeds were extracted with supercritical carbon dioxide at pressures ranging from 15-60 MPa and temperatures of 40-80 degrees C. Oil and β-sitosterol yields were measured in the extraction course and compared with Soxhlet extraction with hexane. The average yield of β-sitosterol was 0.31 mg/g of seeds. The maximum concentration of β-sitosterol in the extract, 0.5% w/w, was achieved at 15 MPa, 40 degrees C, and a carbon dioxide consumption of 50 g/g of seeds. The extraction rate was maximal at 60 MPa and 40 degrees C. Both β-sitosterol yield and its concentration in the extract obtained with hexane were lower than with carbon dioxide.
Keywords: Hippophae rhamnoides L.; fractionation in time; sea buckthorn seed; supercritical carbon dioxide; β-sitosterol.
Figures
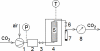
Similar articles
-
Influence of harvest time on the quality of oil-based compounds in sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L. ssp. sinensis) seed and fruit.J Agric Food Chem. 2007 Oct 3;55(20):8054-61. doi: 10.1021/jf070772f. Epub 2007 Aug 31. J Agric Food Chem. 2007. PMID: 17760409
-
Safety and healing efficacy of Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) seed oil on burn wounds in rats.Food Chem Toxicol. 2009 Jun;47(6):1146-53. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2009.02.002. Food Chem Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19425187
-
Fatty acid composition of developing sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) berry and the transcriptome of the mature seed.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034099. Epub 2012 Apr 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22558083 Free PMC article.
-
The beneficial health aspects of sea buckthorn (Elaeagnus rhamnoides (L.) A.Nelson) oil.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Mar 1;213:183-190. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.11.022. Epub 2017 Nov 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29166576 Review.
-
Extraction of volatile oil from aromatic plants with supercritical carbon dioxide: experiments and modeling.Molecules. 2012 Sep 5;17(9):10550-73. doi: 10.3390/molecules170910550. Molecules. 2012. PMID: 22951395 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Protective Effects and Mechanisms of Sea Buckthorn Sterol against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Rats.Molecules. 2022 Mar 29;27(7):2224. doi: 10.3390/molecules27072224. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35408620 Free PMC article.
-
Subcritical dimethyl ether extraction as a simple method to extract nutraceuticals from byproducts from rice bran oil manufacture.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 3;10(1):21007. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78011-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33273543 Free PMC article.
-
Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of the Oak Silkworm (Antheraea pernyi) Pupal Oil: process optimization and composition determination.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(2):2354-2367. doi: 10.3390/ijms13022354. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22408458 Free PMC article.
-
Supercritical CO2 extraction in chia oils production: impact of process duration and co-solvent addition.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2018;27(3):677-686. doi: 10.1007/s10068-018-0316-2. Epub 2018 Jan 17. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29937682 Free PMC article.
-
Supercritical CO2 Extraction of Fatty Acids, Phytosterols, and Volatiles from Myrtle (Myrtus communis L.) Fruit.Molecules. 2024 Apr 12;29(8):1755. doi: 10.3390/molecules29081755. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38675575 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dinan L. Phytoecdysteroids: Biological aspects. Phytochemistry. 2001;57:325–339. - PubMed
-
- Bradford PG, Awad AB. Phytosterols as anticancer compounds. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007;51:161–170. - PubMed
-
- Hicks KB, Moreau RA. Phytosterols and phytostanols: Functional food cholesterol busters. Food Technol. 2001;55:63–67.
-
- Jones PJH, MacDougall DE, Ntanios F, Vanstone CA. Dietary phytosterols as cholesterol-lowering agents in humus. Canad. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1997;75:217–227. - PubMed
-
- Beveridge THJ, Li TSC, Drover JCG. Phytosterol content in American ginseng seed oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002;50:744–750. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

