Structure-activity relationships in human toll-like receptor 7-active imidazoquinoline analogues
- PMID: 20481492
- PMCID: PMC2895411
- DOI: 10.1021/jm100358c
Structure-activity relationships in human toll-like receptor 7-active imidazoquinoline analogues
Abstract
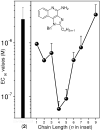
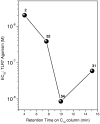
Engagement of toll-like receptors serve to link innate immune responses with adaptive immunity and can be exploited as powerful vaccine adjuvants for eliciting both primary and anamnestic immune responses. TLR7 agonists are highly immunostimulatory without inducing dominant proinflammatory cytokine responses. A structure-activity study was conducted on the TLR7-agonistic imidazoquinolines, starting with 1-(4-amino-2-((ethylamino)methyl)-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-1-yl)-2-methylpropan-2-ol as a lead. Modifications of the secondary amine of the C2 ethylaminomethylene side chain are poorly tolerated. The 4-amino group must be retained for activity. Replacement of the imidazole ring of the scaffold with triazole or cyclic urea led to complete loss of activity. A systematic exploration of N(1)-benzyl-C2-alkyl substituents showed a very distinct relationship between alkyl length and TLR7-agonistic potency with the optimal compound bearing a C2-n-butyl group. Transposition of the N(1) and C2 substituents led to the identification of an extremely active TLR7-agonistic compound with an EC(50) value of 8.6 nM. The relative potencies in human TLR7-based primary reporter gene assays were paralleled by interferon-alpha induction activities in whole human blood models.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptor (TLR)-7 and -8 modulatory activities of dimeric imidazoquinolines.J Med Chem. 2012 Feb 9;55(3):1106-16. doi: 10.1021/jm2010207. Epub 2012 Jan 27. J Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22239408 Free PMC article.
-
Potent adjuvanticity of a pure TLR7-agonistic imidazoquinoline dendrimer.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43612. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043612. Epub 2012 Aug 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952720 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor-8 agonistic activities in C2, C4, and C8 modified thiazolo[4,5-c]quinolines.Org Biomol Chem. 2013 Feb 21;11(7):1179-98. doi: 10.1039/c2ob26705e. Org Biomol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23314908 Free PMC article.
-
The use of Toll-like receptor 7/8 agonists as vaccine adjuvants.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2013 Jul;12(7):809-19. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2013.811208. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2013. PMID: 23885825 Review.
-
TLR7 and TLR8 as targets in cancer therapy.Oncogene. 2008 Jan 7;27(2):190-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210913. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18176600 Review.
Cited by
-
Formulation and preclinical evaluation of a toll-like receptor 7/8 agonist as an anti-tumoral immunomodulator.J Control Release. 2019 Jul 28;306:165-176. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.06.003. Epub 2019 Jun 4. J Control Release. 2019. PMID: 31173789 Free PMC article.
-
Sterilizing Immunity against SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Mice by a Single-Shot and Lipid Amphiphile Imidazoquinoline TLR7/8 Agonist-Adjuvanted Recombinant Spike Protein Vaccine*.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 Apr 19;60(17):9467-9473. doi: 10.1002/anie.202015362. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021. PMID: 33464672 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-activity relationships in human Toll-like receptor 2-specific monoacyl lipopeptides.J Med Chem. 2012 Apr 12;55(7):3353-63. doi: 10.1021/jm3000533. Epub 2012 Mar 15. J Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22385476 Free PMC article.
-
Sterilizing Immunity against SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Mice by a Single-Shot and Modified Imidazoquinoline TLR7/8 Agonist-Adjuvanted Recombinant Spike Protein Vaccine.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Oct 23:2020.10.23.344085. doi: 10.1101/2020.10.23.344085. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 Apr 19;60(17):9467-9473. doi: 10.1002/anie.202015362. PMID: 33106810 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Agonist and antagonist ligands of toll-like receptors 7 and 8: Ingenious tools for therapeutic purposes.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 May 1;193:112238. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112238. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32203790 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. TLR signaling. Semin Immunol. 2007;19:24–32. - PubMed
-
- Kumagai Y, Takeuchi O, Akira S. Pathogen recognition by innate receptors. J Infect Chemother. 2008;14:86–92. - PubMed
-
- Akira S. Innate immunity to pathogens: diversity in receptors for microbial recognition. Immunol Rev. 2009;227:5–8. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Takeda K, Kaisho T. Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nature Immunol. 2001;2:675–680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

