Pd(II)-catalyzed oxidative 1,1-diarylation of terminal olefins
- PMID: 20481606
- PMCID: PMC2908953
- DOI: 10.1021/ol1009575
Pd(II)-catalyzed oxidative 1,1-diarylation of terminal olefins
Abstract
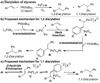
Evaluation of the scope of a Pd(II)-catalyzed oxidative 1,1-diarylation reaction of terminal olefins using aryl stannanes is reported. The reaction is shown to be tolerant of functionality commonly encountered in organic synthesis; however, the reaction outcome was found to be dependent on the nature of the aryl stannane used. A mechanistic rationale for the observation of this influence is provided.
Figures
References
-
-
For an overview of palladium-catalyzed difunctionalization reactions, see: Jensen KH, Sigman MS. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008;6:4083–4088. For an example of palladium-catalyzed arylhalogenation, see: Kalyani D, Sanford MS. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:2150–2151.
-
-
-
For examples of palladium-catalyzed dialkoxylation see Chevrin C, Le Bras J, Henin F, Muzart J. Sythesis. 2005:2615–2628. Schultz MJ, Sigman MS. J Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:1460–1461. Thiery E, Chevrin C, Le Bras J, Harakat D, Muzart J. J. Org. Chem. 2007;72:1859–1862. Zhang Y, Sigman MS. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:3076–3077. Jensen KH, Pathak TP, Zhang Y, Sigman MS. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;131:17074–17075.
-
-
-
For examples of hydrofunctionalization using a similar strategy, see: Gligorich KM, Schultz MJ, Sigman MS. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:2794–2795. Gligorich KM, Cummings SA, Sigman MS. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:14193–14195. Podhajsky SM, Sigman MS. Organometallics. 2007;26:5680–5686. Iwai Y, Gligorich KM, Sigman MS. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008;47:3219–3222. Urkalan KB, Sigman MS. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;131:18042–18043.
-
-
-
For examples of palladium-catalyzed diamination reactions see: Bar GLJ, Lloyd-Jones GC, Booker-Milburn KI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:7308–7309. Du H, Zhao B, Shi Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:762–763. Du H, Yuan W, Zhao B, Shi Y. J. Am Chem. Soc. 2007;129:11688–11689. Xu L, Shi Y. J. Org. Chem. 2008;73:749–751. Du H, Yuan W, Zhao B, Shi Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:7496–7497. Du H, Zhao B, Shi Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:8590–8591.
-
-
-
For examples of nucleopalladation-alkene insertion stratagies see: Arai MA, Kuraishi M, Arai T, Sasai H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001;123:2907–2908. Minami K, Kawamura Y, Koga K, Hosokawa T. Org. Lett. 2005;7:5689–5692. Kawamura Y, Imai T, Hosokawa T. Synlett. 2006:3110–3114. Yip K-T, Yang M, Law K-L, Zhu N-Y, Yang D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:3130–3131. Scarborough CC, Stahl SS. Org. Lett. 2006;8:3251–3254.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources