Biological assessment of triazine dendrimer: toxicological profiles, solution behavior, biodistribution, drug release and efficacy in a PEGylated, paclitaxel construct
- PMID: 20481608
- PMCID: PMC2914493
- DOI: 10.1021/mp100104x
Biological assessment of triazine dendrimer: toxicological profiles, solution behavior, biodistribution, drug release and efficacy in a PEGylated, paclitaxel construct
Abstract
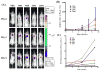
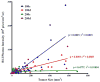
The physicochemical characteristics, in vitro properties, and in vivo toxicity and efficacy of a third generation triazine dendrimer bearing approximately nine 2 kDa polyethylene glycol chains and twelve ester linked paclitaxel groups are reported. The hydrodynamic diameter of the neutral construct varies slightly with aqueous solvent ranging from 15.6 to 19.4 nm. Mass spectrometry and light scattering suggest radically different molecular weights with the former approximately 40 kDa mass consistent with expectation, and the latter 400 kDa mass consistent with a decameric structure and the observed hydrodynamic radii. HPLC can be used to assess purity as well as paclitaxel release, which is insignificant in organic solvents or aqueous solutions at neutral and low pH. Paclitaxel release occurs in vitro in human, rat, and mouse plasma and is nonlinear, ranging from 7 to 20% cumulative release over a 48 h incubation period. The construct is 2-3 orders of magnitude less toxic than Taxol by weight in human hepatocarcinoma (Hep G2), porcine renal proximal tubule (LLC-PK1), and human colon carcinoma (LS174T) cells, but shows similar cytotoxicity to Abraxane in LS174T cells. Both Taxol and the construct appear to induce caspase 3-dependent apoptosis. The construct shows a low level of endotoxin, is not hemolytic and does not induce platelet aggregation in vitro, but does appear to reduce collagen-induced platelet aggregation in vitro. Furthermore, the dendrimer formulation slightly activates the complement system in vitro due most likely to the presence of trace amounts (<1%) of free paclitaxel. An animal study provided insight into the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) wherein 10, 25, 50, and 100 mg of paclitaxel/kg of construct or Abraxane were administered once per week for three consecutive weeks to non tumor bearing athymic nude mice. The construct showed in vivo toxicity comparable to that of Abraxane. Both formulations were found to be nontoxic at the administered doses, and the dendrimer had an acute MTD greater than the highest dose administered. In a prostate tumor model (PC-3-h-luc), efficacy was observed over 70 days with an arrest of tumor growth and lack of luciferase activity observed in the twice treated cohort.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antitumor activity and molecular dynamics simulations of paclitaxel-laden triazine dendrimers.Mol Pharm. 2012 Mar 5;9(3):404-12. doi: 10.1021/mp2005017. Epub 2012 Feb 3. Mol Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22260328 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and biological assessment of a triazine dendrimer with approximately 16 Paclitaxel groups and 8 PEG groups.Mol Pharm. 2013 Dec 2;10(12):4452-61. doi: 10.1021/mp400290u. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Mol Pharm. 2013. PMID: 24134039 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, characterization, and biological evaluation of triazine dendrimers bearing paclitaxel using ester and ester/disulfide linkages.Bioconjug Chem. 2009 Nov;20(11):2154-61. doi: 10.1021/bc900324z. Bioconjug Chem. 2009. PMID: 19877601
-
The role of the size and number of polyethylene glycol chains in the biodistribution and tumor localization of triazine dendrimers.Mol Pharm. 2008 Jul-Aug;5(4):540-7. doi: 10.1021/mp8000292. Mol Pharm. 2008. PMID: 18672950
-
Formulation development and antitumor activity of a filter-sterilizable emulsion of paclitaxel.Pharm Res. 2000 Feb;17(2):175-82. doi: 10.1023/a:1007565230130. Pharm Res. 2000. PMID: 10751032
Cited by
-
Overview of Venous Thromboembolism and Emerging Therapeutic Technologies Based on Nanocarriers-Mediated Drug Delivery Systems.Molecules. 2024 Oct 15;29(20):4883. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204883. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39459251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lessons learned from immunological characterization of nanomaterials at the Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 10;13:984252. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.984252. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36304452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and properties of star-comb polymers and their doxorubicin conjugates.Bioconjug Chem. 2011 Apr 20;22(4):617-24. doi: 10.1021/bc100400u. Epub 2011 Mar 4. Bioconjug Chem. 2011. PMID: 21375296 Free PMC article.
-
Biodistribution and Biosafety of a Poly(Phosphorhydrazone) Dendrimer, an Anti-Inflammatory Drug-Candidate.Biomolecules. 2019 Sep 11;9(9):475. doi: 10.3390/biom9090475. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31514434 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor activity and molecular dynamics simulations of paclitaxel-laden triazine dendrimers.Mol Pharm. 2012 Mar 5;9(3):404-12. doi: 10.1021/mp2005017. Epub 2012 Feb 3. Mol Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22260328 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crown J, O’Leary M, Ooi WS. Docetaxel and paclitaxel in the treatment of breast cancer: a review of clinical experience. Oncologist. 2004;9:24–32. - PubMed
-
- Singla AK, Garg A, Aggarwal D. Paclitaxel and its formulations. Int J Pharm. 2002;235:179–192. - PubMed
-
- Duncan R. The dawning era of polymer therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2003;2:347–360. - PubMed
-
- Putnam D. Drug delivery: the heart of the matter. Nat Mater. 2008;7:836–837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

