Control of cholesterol synthesis through regulated ER-associated degradation of HMG CoA reductase
- PMID: 20482385
- PMCID: PMC2937355
- DOI: 10.3109/10409238.2010.485605
Control of cholesterol synthesis through regulated ER-associated degradation of HMG CoA reductase
Abstract
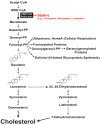
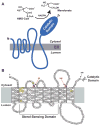
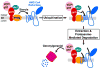
Multiple mechanisms for feedback control of cholesterol synthesis converge on the rate-limiting enzyme in the pathway, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. This complex feedback regulatory system is mediated by sterol and nonsterol metabolites of mevalonate, the immediate product of reductase activity. One mechanism for feedback control of reductase involves rapid degradation of the enzyme from membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). This degradation results from the accumulation of sterols in ER membranes, which triggers binding of reductase to ER membrane proteins called Insig-1 and Insig-2. Insig binding leads to the recruitment of a membrane-associated ubiquitin ligase called gp78 that initiates ubiquitination of reductase. Ubiquitinated reductase then becomes extracted from ER membranes and is delivered to cytosolic 26S proteasomes through an unknown mechanism that is mediated by the gp78-associated ATPase Valosin-containing protein/p97 and appears to be augmented by nonsterol isoprenoids. Here, we will highlight several advances that have led to the current view of mechanisms for sterol-accelerated, ER-associated degradation of reductase. In addition, we will discuss potential mechanisms for other aspects of the pathway such as selection of reductase for gp78-mediated ubiquitination, extraction of the ubiquitinated enzyme from ER membranes, and the contribution of Insig-mediated degradation to overall regulation of reductase in whole animals.
Figures


References
-
- Ahner A, Brodsky JL. Checkpoints in ER-associated degradation: excuse me, which way to the proteasome? Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14:474–478. - PubMed
-
- Altmann SW, Davis, Zhu LJ, Yao X, Hoos LM, et al. Niemann-Pick C1 Like 1 Protein Is Critical for Intestinal Cholesterol Absorption. Science. 2004;303:1201–1204. - PubMed
-
- Aridor M. Visiting the ER: The endoplasmic reticulum as a target for therapeutics in traffic related diseases. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2007;59:759–781. - PubMed
-
- Bartz R, Zehmer JK, Zhu M, Chen Y, Serrero G, et al. Dynamic activity of lipid droplets: protein phosphorylation and GTP-mediated protein translocation 2. J Proteome Res. 2007;6:3256–3265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
