p38 mediates mechanical allodynia in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 20482876
- PMCID: PMC2881061
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-28
p38 mediates mechanical allodynia in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Background: Painful Diabetic Neuropathy (PDN) affects more than 25% of patients with type 2 diabetes; however, the pathogenesis remains unclear due to lack of knowledge of the molecular mechanisms leading to PDN. In our current study, we use an animal model of type 2 diabetes in order to understand the roles of p38 in PDN. Previously, we have demonstrated that the C57BLK db/db (db/db) mouse, a model of type 2 diabetes that carries the loss-of-function leptin receptor mutant, develops mechanical allodynia in the hind paws during the early stage (6-12 wk of age) of diabetes. Using this timeline of PDN, we can investigate the signaling mechanisms underlying mechanical allodynia in the db/db mouse.
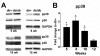
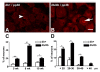
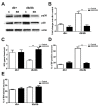
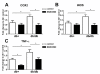
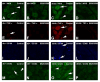
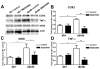
Results: We studied the role of p38 in lumbar dorsal root ganglia (LDRG) during the development of mechanical allodynia in db/db mice. p38 phosphorylation was detected by immunoblots at the early stage of mechanical allodynia in LDRG of diabetic mice. Phosphorylated p38 (pp38) immunoreactivity was detected mostly in the small- to medium-sized LDRG neurons during the time period of mechanical allodynia. Treatment with an antibody against nerve growth factor (NGF) significantly inhibited p38 phosphorylation in LDRG of diabetic mice. In addition, we detected higher levels of inflammatory mediators, including cyclooxygenase (COX) 2, inducible nitric oxide synthases (iNOS), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha in LDRG neurons of db/db mice compared to non-diabetic db+ mice. Intrathecal delivery of SB203580, a p38 inhibitor, significantly inhibited the development of mechanical allodynia and the upregulation of COX2, iNOS and TNF-alpha.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that NGF activated-p38 phosphorylation mediates mechanical allodynia in the db/db mouse by upregulation of multiple inflammatory mediators in LDRG.
Figures
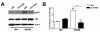

Similar articles
-
Interleukin-10 Reduces Neurogenic Inflammation and Pain Behavior in a Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes.J Pain Res. 2020 Dec 29;13:3499-3512. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S264136. eCollection 2020. J Pain Res. 2020. PMID: 33402846 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve growth factor/p38 signaling increases intraepidermal nerve fiber densities in painful neuropathy of type 2 diabetes.Neurobiol Dis. 2012 Jan;45(1):280-7. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2011.08.011. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Neurobiol Dis. 2012. PMID: 21872660 Free PMC article.
-
Neurogenic factor-induced Langerhans cell activation in diabetic mice with mechanical allodynia.J Neuroinflammation. 2013 May 14;10:64. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-10-64. J Neuroinflammation. 2013. PMID: 23672639 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve growth factor mediates mechanical allodynia in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2009 Nov;68(11):1229-43. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181bef710. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19816194 Free PMC article.
-
Neuron-astrocyte signaling network in spinal cord dorsal horn mediates painful neuropathy of type 2 diabetes.Glia. 2012 Sep;60(9):1301-15. doi: 10.1002/glia.22349. Epub 2012 May 9. Glia. 2012. PMID: 22573263 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-10 Reduces Neurogenic Inflammation and Pain Behavior in a Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes.J Pain Res. 2020 Dec 29;13:3499-3512. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S264136. eCollection 2020. J Pain Res. 2020. PMID: 33402846 Free PMC article.
-
Identify the Key Active Ingredients and Pharmacological Mechanisms of Compound XiongShao Capsule in Treating Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy by Network Pharmacology Approach.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 May 9;2019:5801591. doi: 10.1155/2019/5801591. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31210774 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of TNF-α ameliorates diabetic neuropathy in mice.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Nov;301(5):E844-52. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00029.2011. Epub 2011 Aug 2. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 21810933 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve growth factor/p38 signaling increases intraepidermal nerve fiber densities in painful neuropathy of type 2 diabetes.Neurobiol Dis. 2012 Jan;45(1):280-7. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2011.08.011. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Neurobiol Dis. 2012. PMID: 21872660 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction after Spinal Cord Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 26;24(9):7885. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097885. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Feldman EL, Stevens MJ, Russell JW, Peltier A, Inzucchi S, Porte JD, Sherwin RS, Baron A. The Diabetes Mellitus Manual. Vol. 6. McGraw-Hill; 2005. Somatosensory neuropathy; pp. 366–384.
-
- Singleton JR, Smith AG, Russell J, Feldman EL. Polyneuropathy with Impaired Glucose Tolerance: Implications for Diagnosis and Therapy. CurrTreatOptionsNeurol. 2005;7:33–42. - PubMed
-
- Singleton JR, Smith AG, Bromberg MB. Painful sensory polyneuropathy associated with impaired glucose tolerance. Muscle & nerve. 2005;24:1225–1228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

