Accelerated hand bone mineral density loss is associated with progressive joint damage in hands and feet in recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 20482894
- PMCID: PMC2911882
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3025
Accelerated hand bone mineral density loss is associated with progressive joint damage in hands and feet in recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: To investigate whether accelerated hand bone mineral density (BMD) loss is associated with progressive joint damage in hands and feet in the first year of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and whether it is an independent predictor of subsequent progressive total joint damage after 4 years.
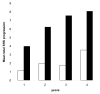
Methods: In 256 recent-onset RA patients, baseline and 1-year hand BMD was measured in metacarpals 2-4 by digital X-ray radiogrammetry. Joint damage in hands and feet were scored in random order according to the Sharp-van der Heijde method at baseline and yearly up to 4 years.
Results: 68% of the patients had accelerated hand BMD loss (>-0.003 g/cm2) in the first year of RA. Hand BMD loss was associated with progressive joint damage after 1 year both in hands and feet with odds ratios (OR) (95% confidence intervals [CI]) of 5.3 (1.3-20.9) and 3.1 (1.0-9.7). In univariate analysis, hand BMD loss in the first year was a predictor of subsequent progressive total joint damage after 4 years with an OR (95% CI) of 3.1 (1.3-7.6). Multivariate analysis showed that only progressive joint damage in the first year and anti-citrullinated protein antibody positivity were independent predictors of long-term progressive joint damage.
Conclusions: In the first year of RA, accelerated hand BMD loss is associated with progressive joint damage in both hands and feet. Hand BMD loss in the first year of recent-onset RA predicts subsequent progressive total joint damage, however not independent of progressive joint damage in the first year.
Figures

References
-
- O'Gradaigh D, Ireland D, Compston JE. Joint erosion in rheumatoid arthritis: interactions between tumour necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1, and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL) regulate osteoclasts. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63:354–359. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.008458. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ainola MM, Mandelin JA, Liljestrom MP, Li T-F, Hukkanen MVJ, Konttinen YT. Pannus invasion and cartilage degradation in rheumatoid arthritis: Involvement of MMP-3 and interleukin-1β. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005;23:644–650. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

