Altered spatiotemporal dynamics of the mitochondrial membrane potential in the hypertrophied heart
- PMID: 20483313
- PMCID: PMC2872265
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.01.045
Altered spatiotemporal dynamics of the mitochondrial membrane potential in the hypertrophied heart
Abstract
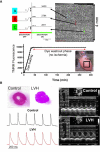
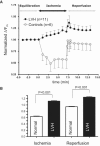
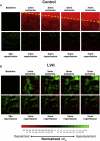
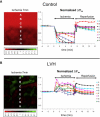
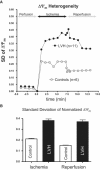
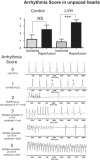
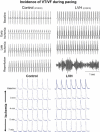
Chronically elevated levels of oxidative stress resulting from increased production and/or impaired scavenging of reactive oxygen species are a hallmark of mitochondrial dysfunction in left ventricular hypertrophy. Recently, oscillations of the mitochondrial membrane potential (DeltaPsi(m)) were mechanistically linked to changes in cellular excitability under conditions of acute oxidative stress produced by laser-induced photooxidation of cardiac myocytes in vitro. Here, we investigate the spatiotemporal dynamics of DeltaPsi(m) within the intact heart during ischemia-reperfusion injury. We hypothesize that altered metabolic properties in left ventricular hypertrophy modulate DeltaPsi(m) spatiotemporal properties and arrhythmia propensity.
Copyright 2010 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress in the mitochondrial matrix underlies ischemia/reperfusion-induced mitochondrial instability.J Biol Chem. 2023 Jan;299(1):102780. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102780. Epub 2022 Dec 7. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 36496071 Free PMC article.
-
The mitochondrial origin of postischemic arrhythmias.J Clin Invest. 2005 Dec;115(12):3527-35. doi: 10.1172/JCI25371. Epub 2005 Nov 10. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 16284648 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise-induced protection against reperfusion arrhythmia involves stabilization of mitochondrial energetics.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016 May 15;310(10):H1360-70. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00858.2015. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26945082 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Role of Mitochondria in Arrhythmogenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;982:191-202. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-55330-6_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28551788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From mitochondrial dynamics to arrhythmias.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Oct;41(10):1940-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.02.016. Epub 2009 Mar 5. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19703656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial targets for arrhythmia suppression: is there a role for pharmacological intervention?J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2013 Sep;37(3):249-58. doi: 10.1007/s10840-013-9809-3. Epub 2013 Jul 4. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2013. PMID: 23824789 Review.
-
Mitochondrial adaptations to physiological vs. pathological cardiac hypertrophy.Cardiovasc Res. 2011 May 1;90(2):234-42. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr015. Epub 2011 Jan 21. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21257612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of mitochondrial depolarization/recovery during ischaemia--reperfusion using spectral properties of confocally recorded TMRM fluorescence.J Physiol. 2013 Jun 1;591(11):2781-94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.248153. Epub 2013 Mar 25. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23529126 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring mitochondrial function in intact cardiac myocytes.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012 Jan;52(1):48-61. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.08.030. Epub 2011 Sep 22. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 21964191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biophysical properties and functional consequences of reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced ROS release in intact myocardium.J Physiol. 2011 Nov 1;589(Pt 21):5167-79. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.214239. Epub 2011 Aug 8. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21825030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kang Y.J. Cardiac hypertrophy: a risk factor for QT-prolongation and cardiac sudden death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2006;34:58–66. - PubMed
-
- Stanley W.C., Chandler M.P. Energy metabolism in the normal and failing heart: potential for therapeutic interventions. Heart Fail. Rev. 2002;7:115–130. - PubMed
-
- Stanley W.C., Recchia F.A., Lopaschuk G.D. Myocardial substrate metabolism in the normal and failing heart. Physiol. Rev. 2005;85:1093–1129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

