Dual mechanisms of allosteric acceleration of the Na(+),K(+)-ATPase by ATP
- PMID: 20483338
- PMCID: PMC2872473
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.01.038
Dual mechanisms of allosteric acceleration of the Na(+),K(+)-ATPase by ATP
Abstract
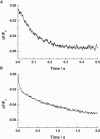
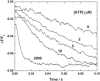
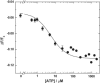
Investigations of the E2 --> E1 conformational change of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase from shark rectal gland and pig kidney via the stopped-flow technique have revealed major differences in the kinetics and mechanisms of the two enzymes. Mammalian kidney Na(+),K(+)-ATPase appears to exist in a diprotomeric (alphabeta)(2) state in the absence of ATP, with protein-protein interactions between the alpha-subunits causing an inhibition of the transition, which occurs as a two-step process: E2:E2 --> E2:E1 --> E1:E1. This is evidenced by a biphasicity in the observed kinetics. Binding of ATP to the E1 or E2 states causes the kinetics to become monophasic and accelerate, which can be explained by an ATP-induced dissociation of the diprotomer into separate alphabeta protomers and relief of the preexisting inhibition. In the case of enzyme from shark rectal gland, the observed kinetics are monophasic at all ATP concentrations, indicating a monoprotomeric enzyme; however, an acceleration of the E2 --> E1 transition by ATP still occurs, to a maximum rate constant of 182 (+/- 6) s(-1). This indicates that ATP has two separate mechanisms whereby it accelerates the E2 --> E1 transition of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase alphabeta protomers and (alphabeta)(2) diprotomers.
Copyright 2010 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Clarke R.J. Mechanism of allosteric effects of ATP on the kinetics of P-type ATPases. Eur. Biophys. J. 2009;39:3–17. - PubMed
-
- Scheiner-Bobis G. The sodium pump. Its molecular properties and mechanics of ion transport. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002;168:123–131. - PubMed
-
- Steinberg M., Karlish S.J.D. Studies on conformational changes in Na,K-ATPase labeled with 5-iodoacetamidofluorescein. J. Biol. Chem. 1989;264:2726–2734. - PubMed
-
- Humphrey P.A., Lüpfert C., Clarke R.J. Mechanism of the rate-determining step of the Na+,K+-ATPase pump cycle. Biochemistry. 2002;41:9496–9507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

