Breaking patterns of environmentally influenced disease for health risk reduction: immune perspectives
- PMID: 20483701
- PMCID: PMC2920092
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.1001971
Breaking patterns of environmentally influenced disease for health risk reduction: immune perspectives
Abstract
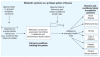
Background: Diseases rarely, if ever, occur in isolation. Instead, most represent part of a more complex web or "pattern" of conditions that are connected via underlying biological mechanisms and processes, emerge across a lifetime, and have been identified with the aid of large medical databases.
Objective: We have described how an understanding of patterns of disease may be used to develop new strategies for reducing the prevalence and risk of major immune-based illnesses and diseases influenced by environmental stimuli.
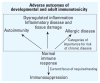
Findings: Examples of recently defined patterns of diseases that begin in childhood include not only metabolic syndrome, with its characteristics of inflammatory dysregulation, but also allergic, autoimmune, recurrent infection, and other inflammatory patterns of disease. The recent identification of major immune-based disease patterns beginning in childhood suggests that the immune system may play an even more important role in determining health status and health care needs across a lifetime than was previously understood.
Conclusions: Focusing on patterns of disease, as opposed to individual conditions, offers two important venues for environmental health risk reduction. First, prevention of developmental immunotoxicity and pediatric immune dysfunction can be used to act against multiple diseases. Second, pattern-based treatment of entryway diseases can be tailored with the aim of disrupting the entire disease pattern and reducing the risk of later-life illnesses connected to underlying immune dysfunction. Disease-pattern-based evaluation, prevention, and treatment will require a change from the current approach for both immune safety testing and pediatric disease management.
Figures



Comment in
-
Breaking patterns of disease: early-life clues may predict long-term health.Environ Health Perspect. 2010 Aug;118(8):a352. doi: 10.1289/ehp.118-2920107. Environ Health Perspect. 2010. PMID: 20675263 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Barone F, Patel P, Sanderson JD, Spencer J. Gut-associated lymphoid tissue contains the molecular machinery to support T-cell-dependent and T-cell-independent class switch recombination. Mucosal Immunol. 2009;2:495–503. - PubMed
-
- Bienenstock J, McDermott MR. Bronchus- and nasal-associated lymphoid tissues. Immunol Rev. 2005;206:22–31. - PubMed
-
- Blood-Siegfried J, Nyska A, Lieder H, Joe M, Vega R, Patterson R, et al. Synergistic effect of influenza A virus on endotoxin-induced mortality in rat pups: a potential model for sudden infant death syndrome. Pediatr Res. 2002;52:481–490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

