B cell development in GALT: role of bacterial superantigen-like molecules
- PMID: 20483765
- PMCID: PMC3419943
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000155
B cell development in GALT: role of bacterial superantigen-like molecules
Abstract
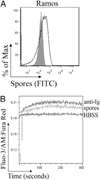
Intestinal bacteria drive the formation of lymphoid tissues, and in rabbit, bacteria also promote development of the preimmune Ab repertoire and positive selection of B cells in GALT. Previous studies indicated that Bacillus subtilis promotes B cell follicle formation in GALT, and we investigated the mechanism by which B. subtilis stimulates B cells. We found that spores of B. subtilis and other Bacillus species, including Bacillus anthracis, bound rabbit IgM through an unconventional, superantigen-like binding site, and in vivo, surface molecules of B. anthracis spores promoted GALT development. Our study provides direct evidence that B cell development in GALT may be driven by superantigen-like molecules, and furthermore, that bacterial spores modulate host immunity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of commensal bacteria in development of gut-associated lymphoid tissues and preimmune antibody repertoire.J Immunol. 2004 Jan 15;172(2):1118-24. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.2.1118. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14707086
-
How host-bacterial interactions lead to IgA synthesis in the gut.Trends Immunol. 2008 Nov;29(11):523-31. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2008.08.001. Trends Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18838301 Review.
-
Significant passive protective effect against anthrax by antibody to Bacillus anthracis inactivated spores that lack two virulence plasmids.Microbiology (Reading). 2006 Oct;152(Pt 10):3103-3110. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28788-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2006. PMID: 17005989
-
Molecular recognition specificity of Bacillus globigii spore antibodies.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2000 Sep;31(3):242-6. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2000.00808.x. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10972737
-
Generating the antibody repertoire in rabbit.Adv Immunol. 1994;56:179-218. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60452-6. Adv Immunol. 1994. PMID: 8073947 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo VL-targeted microbial superantigen induced global shifts in the B cell repertoire.J Immunol. 2012 Jul 15;189(2):850-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200245. Epub 2012 Jun 13. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22696444 Free PMC article.
-
Indoor Airborne Microbial Concentration and Dry Eye.Am J Ophthalmol. 2021 Mar;223:193-204. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2020.10.003. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Am J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33065065 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal Flora and Disease Mutually Shape the Regional Immune System in the Intestinal Tract.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 3;11:575. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00575. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32318067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and Applications of Bacterial Sporulation and Germination in the Intestine.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 21;23(6):3405. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063405. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiota Modulation on Intestinal Mucosal Adaptive Immunity.J Immunol Res. 2019 Oct 3;2019:4735040. doi: 10.1155/2019/4735040. eCollection 2019. J Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 31687412 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hooper LV, Stappenbeck TS, Hong CV, Gordon JI. Angiogenins: a new class of microbicidal proteins involved in innate immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2003;4:269–273. - PubMed
-
- Mazmanian SK, Liu CH, Tzianabos AO, Kasper DL. An immunomodulatory molecule of symbiotic bacteria directs maturation of the host immune system. Cell. 2005;122:107–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

