HLA-F complex without peptide binds to MHC class I protein in the open conformer form
- PMID: 20483783
- PMCID: PMC3777411
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000078
HLA-F complex without peptide binds to MHC class I protein in the open conformer form
Abstract
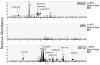
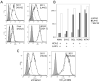
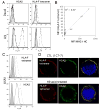
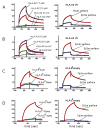
HLA-F has low levels of polymorphism in humans and is highly conserved among primates, suggesting a conserved function in the immune response. In this study, we probed the structure of HLA-F on the surface of B lymphoblastoid cell lines and activated lymphocytes by direct measurement of peptide binding to native HLA-F. Our findings suggested that HLA-F is expressed independently of bound peptide, at least in regard to peptide complexity profiles similar to those of either HLA-E or classical MHC class I (MHC-I). As a further probe of native HLA-F structure, we used a number of complementary approaches to explore the interactions of HLA-F with other molecules, at the cell surface, intracellularly, and in direct physical biochemical measurements. This analysis demonstrated that HLA-F surface expression was coincident with MHC-I H chain (HC) expression and was downregulated upon perturbation of MHC-I HC structure. It was further possible to directly demonstrate that MHC-I would interact with HLA-F only when in the form of an open conformer free of peptide and not as a trimeric complex. This interaction was directly observed by coimmunoprecipitation and by surface plasmon resonance and indirectly on the surface of cells through coincident tetramer and MHC-I HC colocalization. These data suggest that HLA-F is expressed independently of peptide and that a physical interaction specific to MHC-I HC plays a role in the function of MHC-I HC expression in activated lymphocytes.
Figures

References
-
- Accolla RS, Adorini L, Sartoris S, Sinigaglia F, Guardiola J. MHC: orchestrating the immune response. Immunol Today. 1995;16:8–11. - PubMed
-
- Bauer S, Groh V, Wu J, Steinle A, Phillips JH, Lanier LL, Spies T. Activation of NK cells and T cells by NKG2D, a receptor for stress-inducible MICA. Science. 1999;285:727–729. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez S, Groh V, Spies T. Immunobiology of human NKG2D and its ligands. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;298:121–138. - PubMed
-
- Lawlor DA, Zemmour J, Ennis PD, Parham P. Evolution of class-I MHC genes and proteins: from natural selection to thymic selection. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:23–63. - PubMed
-
- Pamer E, Cresswell P. Mechanisms of MHC class I--restricted antigen processing. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:323–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

