The RNA binding protein Tudor-SN is essential for stress tolerance and stabilizes levels of stress-responsive mRNAs encoding secreted proteins in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 20484005
- PMCID: PMC2899877
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.109.070680
The RNA binding protein Tudor-SN is essential for stress tolerance and stabilizes levels of stress-responsive mRNAs encoding secreted proteins in Arabidopsis
Abstract
Tudor-SN (TSN) copurifies with the RNA-induced silencing complex in animal cells where, among other functions, it is thought to act on mRNA stability via the degradation of specific dsRNA templates. In plants, TSN has been identified biochemically as a cytoskeleton-associated RNA binding activity. In eukaryotes, it has recently been identified as a conserved primary target of programmed cell death-associated proteolysis. We have investigated the physiological role of TSN by isolating null mutations for two homologous genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. The double mutant tsn1 tsn2 displays only mild growth phenotypes under nonstress conditions, but germination, growth, and survival are severely affected under high salinity stress. Either TSN1 or TSN2 alone can complement the double mutant, indicating their functional redundancy. TSN accumulates heterogeneously in the cytosol and relocates transiently to a diffuse pattern in response to salt stress. Unexpectedly, stress-regulated mRNAs encoding secreted proteins are significantly enriched among the transcripts that are underrepresented in tsn1 tsn2. Our data also reveal that TSN is important for RNA stability of its targets. These findings show that TSN is essential for stress tolerance in plants and implicate TSN in new, potentially conserved mechanisms acting on mRNAs entering the secretory pathway.
Figures
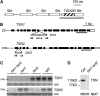
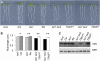
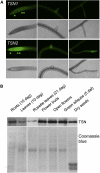



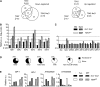


References
-
- Abe S., Sakai M., Yagi K., Hagino T., Ochi K., Shibata K., Davies E. (2003). A Tudor protein with multiple SNc domains from pea seedlings: Cellular localization, partial characterization, sequence analysis, and phylogenetic relationships. J. Exp. Bot. 54: 971–983 - PubMed
-
- Alonso J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Bechtold N., Pelletier G. (1998). In planta Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants by vacuum infiltration. Methods Mol. Biol. 82: 259–266 - PubMed
-
- Bensmihen S., Giraudat J., Parcy F. (2005). Characterization of three homologous basic leucine zipper transcription factors (bZIP) of the ABI5 family during Arabidopsis thaliana embryo maturation. J. Exp. Bot. 56: 597–603 - PubMed
-
- Bensmihen S., To A., Lambert G., Kroj T., Giraudat J., Parcy F. (2004). Analysis of an activated ABI5 allele using a new selection method for transgenic Arabidopsis seeds. FEBS Lett. 561: 127–131 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

