Stress, drugs and the evolution of reproductive restraint in malaria parasites
- PMID: 20484242
- PMCID: PMC2982055
- DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2010.0564
Stress, drugs and the evolution of reproductive restraint in malaria parasites
Abstract
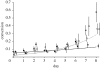
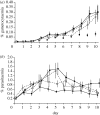
Life-history theory predicts that sexually reproducing organisms have evolved to resolve resource-allocation trade-offs between growth/survival versus reproduction, and current versus future reproduction. Malaria parasites replicate asexually in their vertebrate hosts, but must reproduce sexually to infect vectors and be transmitted to new hosts. As different specialized stages are required for these functions, the division of resources between these life-history components is a fundamental evolutionary problem. Here, we test how drug-sensitive and drug-resistant isolates of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum resolve the trade-off between in-host replication and between-host transmission when exposed to treatment with anti-malarial drugs. Previous studies have shown that parasites increase their investment in sexual stages when exposed to stressful conditions, such as drugs. However, we demonstrate that sensitive parasites facultatively decrease their investment in sexual stages when exposed to drugs. In contrast to previous studies, we tested parasites from a region where treatment with anti-malarial drugs is common and transmission is seasonal. We hypothesize that when exposed to drugs, parasites invest in their survival and future transmission by diverting resources from reproduction to replication. Furthermore, as drug-resistant parasites did not adjust their investment when exposed to drugs, we suggest that parasites respond to changes in their proliferation (state) rather the presence of drugs.
Figures
References
-
- Adjuik M., Babiker A., Garner P., Olliaro P., Taylor W., White N.2004Artesunate combinations for treatment of malaria: metaanalysis. Lancet 363, 9–17 - PubMed
-
- Ali E., Mackinnon M. J., Abdel-Muhsin A. B. A., Ahmed S., Walliker D., Babiker H. A.2006Increased density but not prevalence of gametocytes following drug treatment of Plasmodium falciparum. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 100, 176–183 (doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.04.021) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alizon S., Hurford A., Mideo N., van Baalen M.2009Virulence evolution and the trade-off hypothesis: history, current state of affairs and the future. J. Evol. Biol. 22, 245–259 (doi:10.1111/j.1420-9101.2008.01658.x) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Auld J. R., Agrawal A. A., Relyea R. A.2009Re-evaluating the costs and limits of adaptive phenotypic plasticity. Proc. R. Soc. B 277, 503–511 (doi:10.1098/rspb.2009.1355) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Babiker H. A., Creasey A. M., Fenton B., Bayoumi R. A. L., Arnot D. E., Walliker D.1991Genetic diversity of Plasmodium falciparum in a village in Eastern Sudan. I. Diversity of enzymes, 2D-PAGE proteins and antigens. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 85, 572–577 (doi:10.1016/0035-9203(91)90347-2) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

