Regulation of islet beta-cell pyruvate metabolism: interactions of prolactin, glucose, and dexamethasone
- PMID: 20484462
- PMCID: PMC2903933
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2010-0049
Regulation of islet beta-cell pyruvate metabolism: interactions of prolactin, glucose, and dexamethasone
Abstract
Prolactin (PRL) induces beta-cell proliferation and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) and counteracts the effects of glucocorticoids on insulin production. The mechanisms by which PRL up-regulates GSIS are unknown. We used rat islets and insulinoma (INS-1) cells to explore the interactions of PRL, glucose, and dexamethasone (DEX) in the regulation of beta-cell pyruvate carboxylase (PC), pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), and the pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases (PDKs), which catalyze the phosphorylation and inactivation of PDH. PRL increased GSIS by 37% (P < 0.001) in rat islets. Glucose at supraphysiological concentrations (11 mm) increased PC mRNA in islets; in contrast, PRL suppressed PC mRNA levels in islets and INS-1 cells, whereas DEX was without effect. Neither PRL nor DEX altered PC protein or activity levels. In INS-1 cells, PRL increased PDH activity 1.4- to 2-fold (P < 0.05-0.001) at glucose concentrations ranging from 2.5-11 mm. DEX reduced PDH activity; this effect was reversed by PRL. PDK1, -2, -3, and -4 mRNAs were detected in both islets and insulinoma cells, but the latter expressed trivial amounts of PDK4. PRL reduced PDK2 mRNA and protein levels in rat islets and INS-1 cells and PDK4 mRNA in islets; DEX increased PDK2 mRNA in islets and INS-1 cells; this effect was reversed by PRL. Our findings suggest that PRL induction of GSIS is mediated by increases in beta-cell PDH activity; this is facilitated by suppression of PDKs. PRL counteracts the effects of DEX on PDH and PDK expression, suggesting novel roles for the lactogens in the defense against diabetes.
Figures

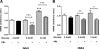
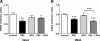
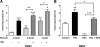
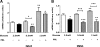
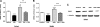
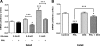
References
-
- Nielsen JH 1982 Effects of growth hormone, prolactin, and placental lactogen on insulin content and release, and deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in cultured pancreatic islets. Endocrinology 110:600–606 - PubMed
-
- Swenne I, Hill DJ, Strain AJ, Milner RD 1987 Effects of human placental lactogen and growth hormone on the production of insulin and somatomedin C/insulin-like growth factor I by human fetal pancreas in tissue culture. J Endocrinol 113:297–303 - PubMed
-
- Brelje TC, Sorenson RL 1991 Role of prolactin versus growth hormone on islet B cell proliferation in vitro: implications for pregnancy. Endocrinology 128:45–57 - PubMed
-
- Brelje TC, Parsons JA, Sorenson RL 1994 Regulation of islet β-cell proliferation by prolactin in rat islets. Diabetes 43:263–273 - PubMed
-
- Møldrup A, Petersen ED, Nielsen JH 1993 Effects of sex and pregnancy hormones on growth hormone and prolactin receptor gene expression in insulin-producing cells. Endocrinology 133:1165– 1172 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

