Identification of novel ribonucleo-protein complexes from the brain-specific snoRNA MBII-52
- PMID: 20484469
- PMCID: PMC2885678
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2109710
Identification of novel ribonucleo-protein complexes from the brain-specific snoRNA MBII-52
Abstract
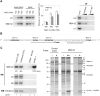
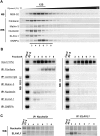
Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) guide nucleotide modifications within ribosomal RNAs or spliceosomal RNAs by base-pairing to complementary regions within their RNA targets. The brain-specific snoRNA MBII-52 lacks such a complementarity to rRNAs or snRNAs, but instead has been reported to target the serotonin receptor 2C pre-mRNA, thereby regulating pre-mRNA editing and/or alternative splicing. To understand how the MBII-52 snoRNA might be involved in these regulatory processes, we isolated the MBII-52 snoRNP from total mouse brain by an antisense RNA affinity purification approach. Surprisingly, by mass spectrometry we identified 17 novel candidates for MBII-52 snoRNA binding proteins, which previously had not been reported to be associated with canonical snoRNAs. Among these, Nucleolin and ELAVL1 proteins were confirmed to independently and directly interact with the MBII-52 snoRNA by coimmunoprecipitation. Our findings suggest that the MBII-52 snoRNA assembles into novel RNA-protein complexes, distinct from canonical snoRNPs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The snoRNA MBII-52 (SNORD 115) is processed into smaller RNAs and regulates alternative splicing.Hum Mol Genet. 2010 Apr 1;19(7):1153-64. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp585. Epub 2010 Jan 6. Hum Mol Genet. 2010. PMID: 20053671 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-specific small nucleolar RNAs.J Mol Neurosci. 2006;28(2):103-9. doi: 10.1385/JMN:28:2:103. J Mol Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16679551 Review.
-
Loss of the imprinted snoRNA mbii-52 leads to increased 5htr2c pre-RNA editing and altered 5HT2CR-mediated behaviour.Hum Mol Genet. 2009 Jun 15;18(12):2140-8. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp137. Epub 2009 Mar 20. Hum Mol Genet. 2009. PMID: 19304781 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of brain-specific and imprinted small nucleolar RNA genes exhibiting an unusual genomic organization.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Dec 19;97(26):14311-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.250426397. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11106375 Free PMC article.
-
The many faces of small nucleolar RNAs.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jun;1839(6):438-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.04.009. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24735946 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional diversity of small nucleolar RNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Feb 28;48(4):1627-1651. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1140. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31828325 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of a patient presumed to have prader-willi syndrome.Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2013 May 5;6:79-86. doi: 10.4137/CCRep.S11510. Print 2013. Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2013. PMID: 23700380 Free PMC article.
-
The cellular landscape of mid-size noncoding RNA.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019 Jul;10(4):e1530. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1530. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019. PMID: 30843375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel role for nucleolin in splice site selection.RNA Biol. 2022;19(1):333-352. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.2020455. Epub 2021 Dec 31. RNA Biol. 2022. PMID: 35220879 Free PMC article.
-
C/D-box snoRNA-derived RNA production is associated with malignant transformation and metastatic progression in prostate cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Jul 10;6(19):17430-44. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4172. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26041889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blencowe BJ, Lamond AI 1999. Purification and depletion of RNP particles by antisense affinity chromatography. In RNA-protein interaction protocols (ed. Haynes SR), pp. 275–287 Humana Press, Totowa, NJ - PubMed
-
- Burns CM, Chu H, Rueter SM, Hutchinson LK, Canton H, Sanders-Bush E, Emeson RB 1997. Regulation of serotonin-2C receptor G-protein coupling by RNA editing. Nature 387: 303–308 - PubMed
-
- Canton H, Emeson RB, Barker EL, Backstrom JR, Lu JT, Chang MS, Sanders-Bush E 1996. Identification, molecular cloning, and distribution of a short variant of the 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptor produced by alternative splicing. Mol Pharmacol 50: 799–807 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
