Upregulation of the chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 via a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike-ACE2 signaling pathway
- PMID: 20484496
- PMCID: PMC2897593
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02560-09
Upregulation of the chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 via a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike-ACE2 signaling pathway
Abstract
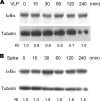
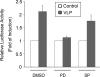
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) was identified to be the causative agent of SARS with atypical pneumonia. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is the major receptor for SARS-CoV. It is not clear whether ACE2 conveys signals from the cell surface to the nucleus and regulates expression of cellular genes upon SARS-CoV infection. To understand the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV, human type II pneumocyte (A549) cells were incubated with the viral spike protein or with SARS-CoV virus-like particles containing the viral spike protein to examine cytokine modulation in lung cells. Results from oligonucleotide-based microarray, real-time PCR, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays indicated an upregulation of the fibrosis-associated chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) by the viral spike protein and the virus-like particles. The upregulation of CCL2 by SARS-CoV spike protein was mainly mediated by extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) and AP-1 but not the IkappaBalpha-NF-kappaB signaling pathway. In addition, Ras and Raf upstream of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway were involved in the upregulation of CCL2. Furthermore, ACE2 receptor was activated by casein kinase II-mediated phosphorylation in cells pretreated with the virus-like particles containing spike protein. These results indicate that SARS-CoV spike protein triggers ACE2 signaling and activates fibrosis-associated CCL2 expression through the Ras-ERK-AP-1 pathway.
Figures









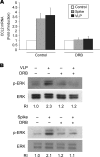

Similar articles
-
Modulation of TNF-alpha-converting enzyme by the spike protein of SARS-CoV and ACE2 induces TNF-alpha production and facilitates viral entry.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jun 3;105(22):7809-14. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0711241105. Epub 2008 May 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18490652 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) from raccoon dog can serve as an efficient receptor for the spike protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.J Gen Virol. 2009 Nov;90(Pt 11):2695-2703. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.013490-0. Epub 2009 Jul 22. J Gen Virol. 2009. PMID: 19625462
-
A study on antigenicity and receptor-binding ability of fragment 450-650 of the spike protein of SARS coronavirus.Virology. 2007 Mar 15;359(2):362-70. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.09.022. Epub 2006 Oct 20. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17055551 Free PMC article.
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus entry as a target of antiviral therapies.Antivir Ther. 2007;12(4 Pt B):639-50. Antivir Ther. 2007. PMID: 17944271 Review.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: a functional receptor for SARS coronavirus.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Nov;61(21):2738-43. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-4242-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15549175 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytokine storm-calming property of the isoquinoline alkaloids in Coptis chinensis Franch.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 6;13:973587. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.973587. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36147356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential role of ACE2-related microRNAs in COVID-19-associated nephropathy.Noncoding RNA Res. 2020 Dec;5(4):153-166. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2020.09.001. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Noncoding RNA Res. 2020. PMID: 32923747 Free PMC article.
-
Into the eye of the cytokine storm.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012 Mar;76(1):16-32. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.05015-11. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22390970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Exploration of Nanoparticle-Based Diagnostic Approaches for Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Oct 11;12(20):3550. doi: 10.3390/nano12203550. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36296739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 spike spurs intestinal inflammation via VEGF production in enterocytes.EMBO Mol Med. 2022 May 9;14(5):e14844. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202114844. Epub 2022 Apr 19. EMBO Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35362189 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang, L., and M. Karin. 2001. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 410:37-40. - PubMed
-
- Chang, Y. J., C. Y. Liu, B. L. Chiang, Y. C. Chao, and C. C. Chen. 2004. Induction of IL-8 release in lung cells via activator protein-1 by recombinant baculovirus displaying severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus spike proteins: identification of two functional regions. J. Immunol. 173:7602-7614. - PubMed
-
- Cheung, C. Y., L. L. Poon, I. H. Ng, W. Luk, S. F. Sia, M. H. Wu, K. H. Chan, K. Y. Yuen, S. Gordon, Y. Guan, and J. S. Peiris. 2005. Cytokine responses in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-infected macrophages in vitro: possible relevance to pathogenesis. J. Virol. 79:7819-7826. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

