Differential activation of NK cells by influenza A pseudotype H5N1 and 1918 and 2009 pandemic H1N1 viruses
- PMID: 20484512
- PMCID: PMC2897595
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00069-10
Differential activation of NK cells by influenza A pseudotype H5N1 and 1918 and 2009 pandemic H1N1 viruses
Abstract
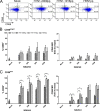
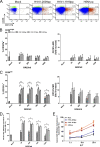
Natural killer (NK) cells are the effectors of innate immunity and are recruited into the lung 48 h after influenza virus infection. Functional NK cell activation can be triggered by the interaction between viral hemagglutinin (HA) and natural cytotoxicity receptors NKp46 and NKp44 on the cell surface. Recently, novel subtypes of influenza viruses, such as H5N1 and 2009 pandemic H1N1, transmitted directly to the human population, with unusual mortality and morbidity rates. Here, the human NK cell responses to these viruses were studied. Differential activation of heterogeneous NK cells (upregulation of CD69 and CD107a and gamma interferon [IFN-gamma] production as well as downregulation of NKp46) was observed following interactions with H5N1, 1918 H1N1, and 2009 H1N1 pseudotyped particles (pps), respectively, and the responses of the CD56(dim) subset predominated. Much stronger NK activation was triggered by H5N1 and 1918 H1N1 pps than by 2009 H1N1 pps. The interaction of pps with NK cells and subsequent internalization were mediated by NKp46 partially. The NK cell activation by pps showed a dosage-dependent manner, while an increasing viral HA titer attenuated NK activation phenotypes, cytotoxicity, and IFN-gamma production. The various host innate immune responses to different influenza virus subtypes or HA titers may be associated with disease severity.
Figures
References
-
- Alter, G., J. M. Malenfant, and M. Altfeld. 2004. CD107a as a functional marker for the identification of natural killer cell activity. J. Immunol. Methods 294:15-22. - PubMed
-
- Arnon, T. I., H. Achdout, N. Lieberman, R. Gazit, T. Gonen-Gross, G. Katz, A. Bar-Ilan, N. Bloushtain, M. Lev, A. Joseph, E. Kedar, A. Porgador, and O. Mandelboim. 2004. The mechanisms controlling the recognition of tumor- and virus-infected cells by NKp46. Blood 103:664-672. - PubMed
-
- Becker, I., N. Salaiza, and M. Aguirre. 2003. Leishmania lipophosphoglycan (LPG) activates NK cells through toll like receptor 2. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 130:65-74. - PubMed
-
- Biassoni, R. 1999. The murine homologue of the human NKp46, a triggering receptor involved in the induction of natural cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Immunol. 29:1014-1020. - PubMed
-
- Bottino, C., R. Biassoni, R. Millo, L. Moretta, and A. Moretta. 2000. The human natural cytotoxicity receptors (NCR) that induce HLA class I independent NK cell triggering. Hum. Immunol. 61:1-6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

