Liver X receptor agonist treatment ameliorates amyloid pathology and memory deficits caused by high-fat diet in APP23 mice
- PMID: 20484628
- PMCID: PMC2883862
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1051-10.2010
Liver X receptor agonist treatment ameliorates amyloid pathology and memory deficits caused by high-fat diet in APP23 mice
Abstract
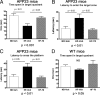
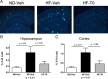
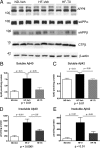
High-fat diet and certain dietary patterns are associated with higher incidence of sporadic Alzheimer's disease (AD) and cognitive decline. However, no specific therapy has been suggested to ameliorate the negative effects of high fat/high cholesterol levels on cognition and amyloid pathology. Here we show that in 9-month-old APP23 mice, a high-fat/high-cholesterol (HF) diet provided for 4 months exacerbates the AD phenotype evaluated by behavioral, morphological, and biochemical assays. To examine the therapeutic potential of liver X receptor (LXR) ligands, APP23 mice were fed HF diet supplemented with synthetic LXR agonist T0901317 (T0). Our results demonstrate that LXR ligand treatment causes a significant reduction of memory deficits observed during both acquisition and retention phases of the Morris water maze. Moreover, the effects of T0 on cognition correlate with AD-like morphological and biochemical parameters. We found a significant decrease in amyloid plaque load, insoluble Abeta and soluble Abeta oligomers. In vitro experiments with primary glia demonstrate that Abca1 is essential for the proper lipidation of ApoE and mediates the effects of T0 on Abeta degradation by microglia. Microdialysis experiments performed on awake freely moving mice showed that T0 decreased Abeta levels in the interstitial fluid of the hippocampus, supporting the conclusion that this treatment increases Abeta clearance. The data presented conclusively shows that LXR activation in the context of a metabolic challenge has critical effects on AD phenotype progression by attenuating Abeta deposition and facilitating its clearance.
Figures





References
-
- Cirrito JR, May PC, O'Dell MA, Taylor JW, Parsadanian M, Cramer JW, Audia JE, Nissen JS, Bales KR, Paul SM, DeMattos RB, Holtzman DM. In vivo assessment of brain interstitial fluid with microdialysis reveals plaque-associated changes in amyloid-beta metabolism and half-life. J Neurosci. 2003;23:8844–8853. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Small GW, Roses AD, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993;261:921–923. - PubMed
-
- George AJ, Holsinger RMD, McLean CA, Laughton KM, Beyreuther K, Evin G, Masters CL, Li QX. APP intracellular domain is increased and soluble A[beta] is reduced with diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2004;16:124–132. - PubMed
-
- Grefhorst A, Elzinga BM, Voshol PJ, Plösch T, Kok T, Bloks VW, van der Sluijs FH, Havekes LM, Romijn JA, Verkade HJ, Kuipers F. Stimulation of lipogenesis by pharmacological activation of the liver X receptor leads to production of large, triglyceride-rich very low density lipoprotein particles. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:34182–34190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
