11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 expression is increased in the aged mouse hippocampus and parietal cortex and causes memory impairments
- PMID: 20484633
- PMCID: PMC2885438
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0731-10.2010
11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 expression is increased in the aged mouse hippocampus and parietal cortex and causes memory impairments
Abstract
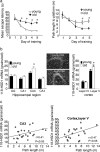
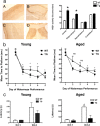
Increased neuronal glucocorticoid exposure may underlie interindividual variation in cognitive function with aging in rodents and humans. 11beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11beta-HSD1) catalyzes the regeneration of active glucocorticoids within cells (in brain and other tissues), thus amplifying steroid action. We examined whether 11beta-HSD1 plays a role in the pathogenesis of cognitive deficits associated with aging in male C57BL/6J mice. We show that 11beta-HSD1 levels increase with age in CA3 hippocampus and parietal cortex, correlating with impaired cognitive performance in the water maze. In contrast, neither circulating corticosterone levels nor tissue corticosteroid receptor expression correlates with cognition. 11beta-HSD1 elevation appears causal, since aging (18 months) male transgenic mice with forebrain-specific 11beta-HSD1 overexpression ( approximately 50% in hippocampus) exhibit premature age-associated cognitive decline in the absence of altered circulating glucocorticoid levels or other behavioral (affective) deficits. Thus, excess 11beta-HSD1 in forebrain is a cause of as well as a therapeutic target in memory impairments with aging.
Figures
References
-
- Casu MA, Wong TP, De Koninck Y, Ribeiro-da-Silva A, Cuello AC. Aging causes a preferential loss of cholinergic innervation of characterized neocortical pyramidal neurons. Cereb Cortex. 2002;12:329–337. - PubMed
-
- Chapman KE, Seckl JR. 11beta-HSD1, inflammation, metabolic disease and age-related cognitive (dys)function. Neurochem Res. 2008;33:624–636. - PubMed
-
- Conrad CD, Galea LA, Kuroda Y, McEwen BS. Chronic stress impairs rat spatial memory on the Y maze, and this effect is blocked by tianeptine pretreatment. Behav Neurosci. 1996;110:1321–1334. - PubMed
-
- Conrad CD, McLaughlin KJ, Harman JS, Foltz C, Wieczorek L, Lightner E, Wright RL. Chronic glucocorticoids increase hippocampal vulnerability to neurotoxicity under conditions that produce CA3 dendritic retraction but fail to impair spatial recognition memory. J Neurosci. 2007;27:8278–8285. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
