The neural and vascular effects of killed Su-Streptococcus pyogenes (OK-432) in preterm fetal sheep
- PMID: 20484698
- PMCID: PMC2928612
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00116.2010
The neural and vascular effects of killed Su-Streptococcus pyogenes (OK-432) in preterm fetal sheep
Abstract
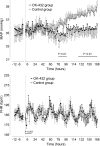
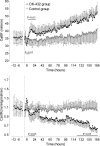
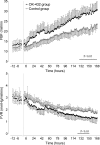
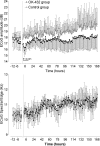
Fetal exposure to inflammatory mediators is associated with a greater risk of brain injury and may cause endothelial dysfunction; however, nearly all the evidence is derived from gram-negative bacteria. Intrapleural injections of OK-432, a killed Su-strain of Streptococcus pyogenes, has been used to treat fetal chylothorax. In this study, we evaluated the neural and cardiovascular effects of OK-432 in preterm fetal sheep (104 +/- 1 days, term 147 days). OK-432 (0.1 mg, n = 6) or saline vehicle (n = 7) was infused in the fetal pleura, and fetuses were monitored for 7 days. Blood samples were taken routinely for plasma nitrite measurement. Fetal brains were taken for histological assessment at the end of the experiment. Between 3 and 7 h postinjection, OK-432 administration was associated with transient suppression of fetal body and breathing movements and electtroencephalogram activity (P < 0.05), increased carotid and femoral vascular resistance (P < 0.05), but no change in blood pressure. Brain activity and behavior then returned to normal except in one fetus that developed seizures. OK-432 fetuses showed progressive, sustained vasodilatation (P < 0.05), with lower blood pressure after 4 days (P < 0.05), but normal heart rate. There were no changes in plasma nitrite levels. Histological studies showed bilateral infarction in the dorsal limb of the hippocampus of the fetus that developed seizures, but no injury in other fetuses. We conclude that a single low-dose injection of OK-432 can be associated with risk of focal cerebral injury in the preterm fetus and chronic central and peripheral vasodilatation that does not appear to be mediated by nitric oxide.
Figures

References
-
- Auvin S, Shin D, Mazarati A, Nakagawa J, Miyamoto J, Sankar R. Inflammation exacerbates seizure-induced injury in the immature brain. Epilepsia 48: 27–34, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Barlow RM. The foetal sheep: morphogenesis of the nervous system and histochemical aspects of myelination. J Comp Neurol 135: 249–262, 1969 - PubMed
-
- Bennet L, Dean JM, Wassink G, Gunn AJ. Differential effects of hypothermia on early and late epileptiform events after severe hypoxia in preterm fetal sheep. J Neurophysiol 97: 572–578, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Bennet L, Roelfsema V, Dean J, Wassink G, Power GG, Jensen EC, Gunn AJ. Regulation of cytochrome oxidase redox state during umbilical cord occlusion in preterm fetal sheep. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 292: R1569–R1576, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Blad S, Welin AK, Kjellmer I, Rosen KG, Mallard C. ECG and heart rate variability changes in preterm and near-term fetal lamb following LPS exposure. Reprod Sci 15: 572–583, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

