Androgen receptor promotes hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocarcinogenesis through modulation of hepatitis B virus RNA transcription
- PMID: 20484730
- PMCID: PMC3032595
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3001143
Androgen receptor promotes hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocarcinogenesis through modulation of hepatitis B virus RNA transcription
Abstract
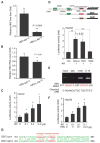
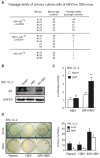
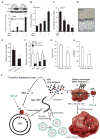
Hepatitis B virus (HBV)-induced hepatitis and carcinogen-induced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are associated with serum androgen concentration. However, how androgen or the androgen receptor (AR) contributes to HBV-induced hepatocarcinogenesis remains unclear. We found that hepatic AR promotes HBV-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in HBV transgenic mice that lack AR only in the liver hepatocytes (HBV-L-AR(-/y)). HBV-L-AR(-/y) mice that received a low dose of the carcinogen N'-N'-diethylnitrosamine (DEN) have a lower incidence of HCC and present with smaller tumor sizes, fewer foci formations, and less alpha-fetoprotein HCC marker than do their wild-type HBV-AR(+/y) littermates. We found that hepatic AR increases the HBV viral titer by enhancing HBV RNA transcription through direct binding to the androgen response element near the viral core promoter. This activity forms a positive feedback mechanism with cooperation with its downstream target gene HBx protein to promote hepatocarcinogenesis. Administration of a chemical compound that selectively degrades AR, ASC-J9, was able to suppress HCC tumor size in DEN-HBV-AR(+/y) mice. These results demonstrate that targeting the AR, rather than the androgen, could be developed as a new therapy to battle HBV-induced HCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Chen CJ, Yu MW, Liaw YF. Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1997;12:S294–S308. - PubMed
-
- Chen CJ, Yang HI, Iloeje UH. REVEAL-HBV Study Group, Hepatitis B virus DNA levels and outcomes in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2009;49:S72–S84. - PubMed
-
- Yu MW, Yang YC, Yang SY, Cheng SW, Liaw YF, Lin SM, Chen CJ. Hormonal markers and hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma risk: A nested case–control study among men. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:1644–1651. - PubMed
-
- Yu MW, Cheng SW, Lin MW, Yang SY, Liaw YF, Chang HC, Hsiao TJ, Lin SM, Lee SD, Chen PJ, Liu CJ, Chen CJ. Androgen-receptor gene CAG repeats, plasma testosterone levels, and risk of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:2023–2028. - PubMed
-
- Lee CM, Lu SN, Changchien CS, Yeh CT, Hsu TT, Tang JH, Wang JH, Lin DY, Chen CL, Chen WJ. Age, gender, and local geographic variations of viral etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in a hyperendemic area for hepatitis B virus infection. Cancer. 1999;86:1143–1150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

