Conversion to gastric bypass in patients with unsuccessful weight loss after gastric banding may depend on mental quality of life
- PMID: 20484946
- PMCID: PMC6452169
- DOI: 10.1159/000295101
Conversion to gastric bypass in patients with unsuccessful weight loss after gastric banding may depend on mental quality of life
Abstract
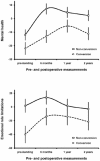
Background: A low quality of life has been regarded a cue to action. Some patients with unsuccessful weight loss after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) undergo a conversion of gastric banding to gastric by-pass. This study examines whether patients who did or did not undergo conversion to gastric bypass differed in quality of life before and after gastric banding.
Methods: Of 34 patients with unsuccessful weight loss after gastric banding (excess body mass index loss < 25%), 14 had a conversion to gastric bypass 2 years or more after gastric banding. All patients completed the RAND-36 quality of life questionnaire before gastric banding. After gastric banding, 24 patients (70.6%) filled out the RAND-36 at 6, 12, and 24 months.
Results: Pre-banding and postbanding mental quality of life was lower in the conversion compared to the non-conversion group.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that a relatively stable lower mental quality of life is a signal for further intervention. The bariatric team and patients should be aware that mental health may play a role in the decision for conversion to gastric bypass. The possible mechanisms underlying this finding, and limitations of the study are discussed.
Copyright 2010 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
References
-
- Salameh JR. Bariatric surgery: past and present. Am J Med Sci. 2006;331:194–200. - PubMed
-
- Saber AA, Elgamal MH, McLeod MK. Bariatric surgery: the pastpresent, and future. Obes Surg. 2008;18:121–128. - PubMed
-
- Chapman AE, Kiroff G, Game P, Foster B, O’Brien P, Ham J, Maddern GJ. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in the treatment of obesity: a systematic literature review. Surgery. 2004;135:326–351. - PubMed
-
- Gagner MGumbs AAGastric banding. conversion to sleevebypass, or DS. Surg Endosc. 2007;21:1931–1935. - PubMed
-
- Kothari SN, DeMaria EJ, Sugerman HJ, Kellum JM, Meador J, Wolfe L. Lap-band failures: conversion to gastric bypass and their preliminary outcomes. Surgery. 2002;131:625–629. - PubMed