Use of a fermented dairy probiotic drink containing Lactobacillus casei (DN-114 001) to decrease the rate of illness in kids: the DRINK study. A patient-oriented, double-blind, cluster-randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial
- PMID: 20485304
- PMCID: PMC2906750
- DOI: 10.1038/ejcn.2010.65
Use of a fermented dairy probiotic drink containing Lactobacillus casei (DN-114 001) to decrease the rate of illness in kids: the DRINK study. A patient-oriented, double-blind, cluster-randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial
Abstract
Background: To evaluate whether a fermented dairy drink containing the probiotic strain Lactobacillus casei DN-114 001 could reduce the incidence of common infectious diseases (CIDs) and the change of behavior because of illness in children.
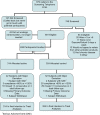
Subjects/methods: We conducted a double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled allocation concealment clinical trial in the Washington, DC metropolitan area. Participants were 638 children 3-6 years old in daycare/schools. The intervention was a fermented dairy drink containing a specific probiotic strain or matching placebo with no live cultures for 90 consecutive days. Two primary outcomes were assessed: incidence of CIDs and change of behavior because of illness (both assessed by parental report).
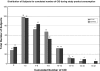
Results: The rate of change of behavior because of illness was similar among active and control groups. However, the incidence rate for CIDs in the active group (0.0782) is 19% lower than that of the control group (0.0986) (incidence rate ratio=0.81, 95% CI: 0.65, 099) P=0.046.
Conclusions: Daily intake of a fermented dairy drink containing the probiotic strain L. casei DN-114 001 showed some promise in reducing overall incidence of illness, but was primarily driven by gastrointestinal infections and there were no differences in change of behavior.
Figures
References
-
- Agarwal KN, Bhasin SK. Feasibility studies to control acute diarrhoea in children by feeding fermented milk preparations Actimel and Indian Dahi. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2002;56 (Suppl 4:S56–S59. - PubMed
-
- Baba N, Samson S, Bourdet-Sicard R, Rubio M, Sarfati M. Selected commensal-related bacteria and toll-like receptor 3 agonist combinatorial codes synergistically induce interleukin-12 production by dendritic cells to trigger a T helper type 1 polarizing programme. Immunology. 2009;128:e523–e531. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cordell RL, MacDonald JK, Solomon SL, Jackson LA, Boase J. Illnesses and absence due to illness among children attending child care facilities in Seattle-King County, Washington. Pediatrics. 1997;100:850–855. - PubMed
-
- Dales R, Cakmak S, Brand K, Judek S. Respiratory illness in children attending daycare. Pediatric Pulmonology. 2004;38:6409. - PubMed
-
- de Moreno de LeBlanc A, Chaves S, Carmuega E, Weill R, Antoine J, Perdigon G. Effect of long-term continuous consumption of fermented milk containing probiotic bacteria on mucosal immunity and the activity of peritoneal macrophages. Immunobiology. 2008;213:97–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical