Opposing roles for calcineurin and ATF3 in squamous skin cancer
- PMID: 20485437
- PMCID: PMC3050632
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08996
Opposing roles for calcineurin and ATF3 in squamous skin cancer
Abstract
Calcineurin inhibitors such as cyclosporin A (CsA) are the mainstay of immunosuppressive treatment for organ transplant recipients. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the skin is a major complication of treatment with these drugs, with a 65 to 100-fold higher risk than in the normal population. By contrast, the incidence of basal cell carcinoma (BCC), the other major keratinocyte-derived tumour of the skin, of melanoma and of internal malignancies increases to a significantly lesser extent. Here we report that genetic and pharmacological suppression of calcineurin/nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) function promotes tumour formation in mouse skin and in xenografts, in immune compromised mice, of H-ras(V12) (also known as Hras1)-expressing primary human keratinocytes or keratinocyte-derived SCC cells. Calcineurin/NFAT inhibition counteracts p53 (also known as TRP53)-dependent cancer cell senescence, thereby increasing tumorigenic potential. ATF3, a member of the 'enlarged' AP-1 family, is selectively induced by calcineurin/NFAT inhibition, both under experimental conditions and in clinically occurring tumours, and increased ATF3 expression accounts for suppression of p53-dependent senescence and enhanced tumorigenic potential. Thus, intact calcineurin/NFAT signalling is critically required for p53 and senescence-associated mechanisms that protect against skin squamous cancer development.
Figures
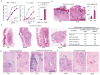
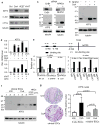
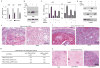
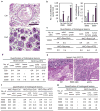
References
-
- Euvrard S, Kanitakis J, Claudy A. Skin cancers after organ transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1681–1691. - PubMed
-
- Mammucari C, et al. Integration of Notch 1 and calcineurin/NFAT signaling pathways in keratinocyte growth and differentiation control. Dev Cell. 2005;8:665–676. - PubMed
-
- Aramburu J, et al. Affinity-driven peptide selection of an NFAT inhibitor more selective than cyclosporin A. Science. 1999;285:2129–2133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

